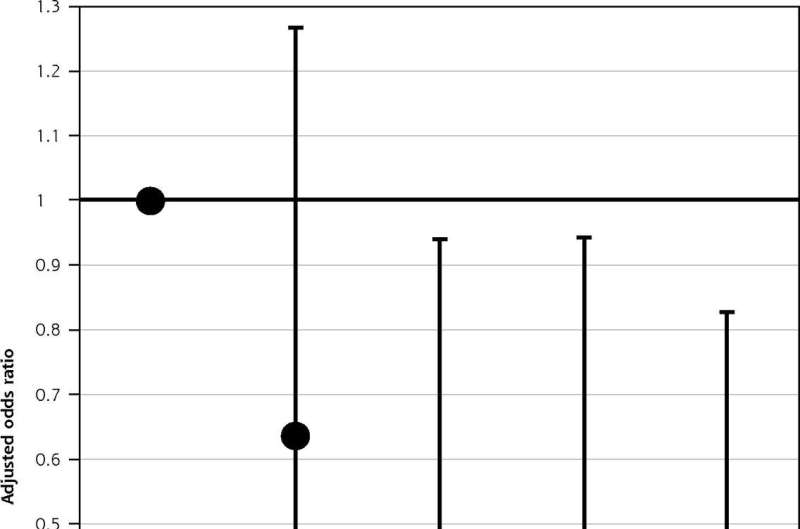
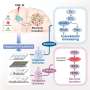
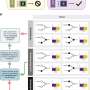
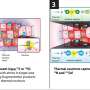
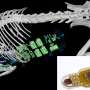
Association between the overall measure of primary care attributes and hospitalization. EQ-5D-5L = 5-level version of the EuroQol 5-dimensional questionnaire; JPCAT = Japanese version of Primary Care Assessment Tool; Q = quartile. Notes: Association assessed by the JPCAT total score. Adjusted for age, sex, educational level, number of chronic conditions, and EQ-5D-5L. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. JPCAT total score quartiles: Q1, 0.0-35.4; Q2, 35.4-47.9; Q3, 47.9-60.4; Q4, 60.4-100.0. Credit: The Annals of Family Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1370/afm.2894
Japanese researchers examined the association between primary care practice characteristics and total hospitalizations during the COVID-19 pandemic. They conducted a nationwide study and examined data from 1,161 participants ages 40-75.
They assessed the quality of primary care attributes, including first contact between the patient and a primary care clinician, length of care, care coordination, comprehensiveness and the clinic's orientation in the community. Researchers primarily sought to identify any hospitalizations among participants during a 12-month period between May 2021 and April 2022.
Each primary care attribute—such as accessibility, continuity, coordination and comprehensiveness—was associated with a reduction in hospitalizations. High-quality primary care was associated with decreased total hospitalizations, even during a pandemic when there are many barriers to providing routine medical care.
The authors argued that these findings support policies intended to strengthen primary care systems during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The integration of public health practice with the delivery of primary care services may be a more important process, especially during a pandemic.
The study is published in The Annals of Family Medicine.
More information: Takuya Aoki et al, Impact of Primary Care Attributes on Hospitalization During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationwide Prospective Cohort Study in Japan, The Annals of Family Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1370/afm.2894
Journal information: Annals of Family Medicine
Provided by American Academy of Family Physicians