During 2022, the incidence of pathogens commonly transmitted through food generally increased to prepandemic levels, according to research published in the June 30 issue of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Miranda J. Delahoy, Ph.D., from the CDC in Atlanta, and colleagues conducted surveillance for laboratory-diagnosed infections caused by eight pathogens transmitted commonly through food at 10 U.S. sites to examine progress toward prevention of enteric infections in the United States.
The researchers observed decreases in many infections during 2020 to 2021 as a result of behavioral modifications, public health interventions, changes in health care seeking, and testing practices during the COVID-19 pandemic. Many of these interventions ended in 2022, resulting in renewal of outbreaks, international travel, and other factors resulting in enteric infections.
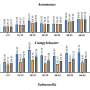
The annual incidences of illnesses caused by Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, and Listeria during 2022 were similar to average annual incidences during 2016 to 2018; higher incidences of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, Yersinia, Vibrio, and Cyclospora illnesses were observed. Increasing use of a culture-independent diagnostic test likely contributed to increased detection by identifying infections that would have remained undetected.
"Progress in reducing enteric infection incidence was not observed during 2022, as influences of the COVID-19 pandemic subsided," the authors write. "Collaboration among food growers, processors, retail stores, restaurants, and regulators is needed to reduce pathogen contamination during poultry slaughter and to prevent contamination of leafy greens."
More information: Miranda J. Delahoy et al, Preliminary Incidence and Trends of Infections Caused by Pathogens Transmitted Commonly Through Food—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 U.S. Sites, 2022, MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2023). DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7226a1
Journal information: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.