There is genetic evidence supporting a causal effect of diastolic blood pressure (DBP) on benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), according to a study published online July 16 in The Prostate.
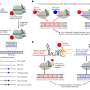
Kaikai Lv, M.D., from The Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital in Beijing, and colleagues conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study to examine the causality of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and its components on BPH using summary-level data from genome-wide association studies. Data were included for 26,358 BPH cases and 110,070 controls.
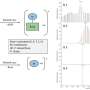
The researchers observed significant positive associations for genetically predicted waist circumference and DBP with BPH risk. No causal effect was seen for MetS, systolic blood pressure, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, or fasting blood glucose on BPH. The risk effect of DBP on BPH persisted after conditioning with waist circumference in the multivariable MR analysis, but no significant association for waist circumference was observed.
"Our MR study provides genetic evidence supporting the causal effect of DBP on BPH. However, the role of increased waist circumference in the risk of developing BPH requires further validation," the authors write. "Our results suggest that the management of DBP may prevent BPH development."
More information: Kaikai Lv et al, The causal effect of metabolic syndrome and its components on benign prostatic hyperplasia: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study, The Prostate (2023). DOI: 10.1002/pros.24598
2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.