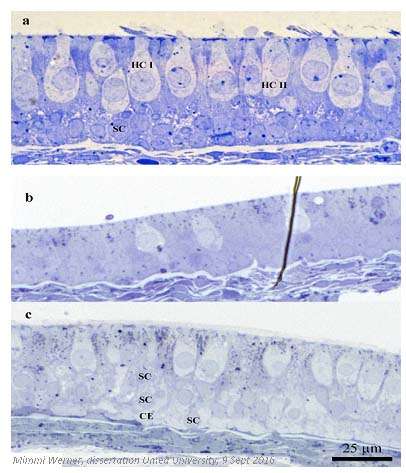
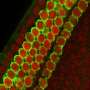
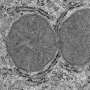
Microscopic portrayal of the balance organ showing the lightly stained hair cells at the top of the epithelium (tissue) and the darker stained supporting cells surrounding the hair cells. (A) Before adding an antibiotic. (B) Only a few hair cells remain after 24 hours. (C) Clear regeneration of hair cells is seen after 17 days. Credit: Mimmi Werner
Research at Umeå University in Sweden shows that in the utricle – which is one of the internal ear's balance organs in mammals – epithelial cells can be regenerated, resulting in healthy sensory hair cells and surrounding supporting cells.
A recent doctoral dissertation presents research showing that, in the balance organ, sensory receptor cells that had died after being subjected to an antibiotic could be replaced after some time post-trauma. According to the results, the supporting cells undergo a gradual change and develop into new sensory receptor cells without undergoing any additional cell division.
"Balance issues are common, in particular among the older population, and may in many cases be due to damage to the sensory cells within the utricle or other parts of the balance organs," says Mimmi Werner, doctoral student at the Department of Clinical Sciences and author of the dissertation.
"The supporting cells are to a certain extent able to transform into sensory receptor cells and if this ability could be stimulated, many people would get help in regaining their balance."
In her research, Mimmi Werner has grown entire utricles in four weeks' time. By adding an antibiotic poisonous to sensory receptors, the researcher has been able to study the process of cell regeneration and its effect on sensory hair cells and supporting cells.
In conclusion, the result shows that both sensory hair cells and supporting cells survive well during long-term cultivation. When adding a poisonous antibiotic, the majority of sensory cells die. Subsequently, supporting cells very rapidly fill in the space of the dead sensory hair cells. After about two weeks, some of the supporting cells start transforming to new sensory receptor cells (pictured).
More information: The thesis is online: umu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/ … 48823/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Provided by Umea University