Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain
Investigators have implemented an automated health maintenance tool created by the National Kidney Foundation into electronic medical records to prompt primary care physicians to screen for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in adult patients with type 2 diabetes. The impact of the tool will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 from November 1–November 5.
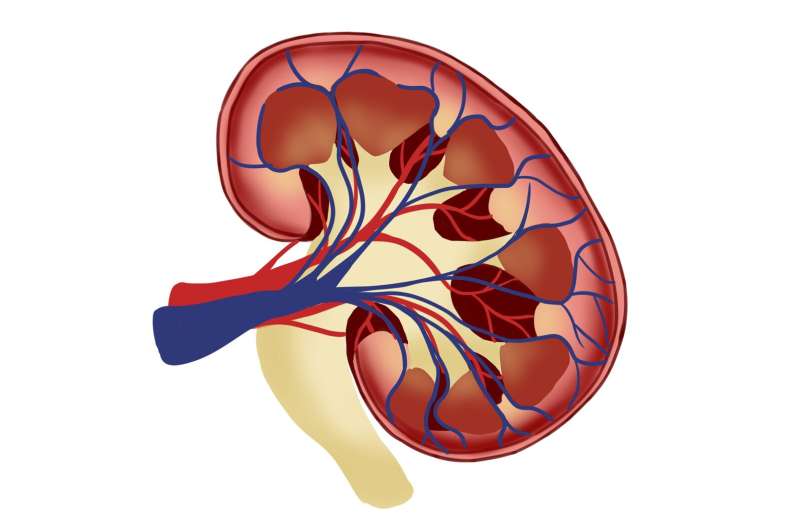
Diabetes is a major cause of CKD, and current guidelines recommend annual kidney function screening in patients with type 2 diabetes. To improve screening, researchers adapted their clinical decision support tool to auto-enroll all adult patients with type 2 diabetes and include an automatic prompt for one-click ordering of kidney function screening tests, such as the urine-albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR, a sign of kidney dysfunction) or the Kidney Profile that includes both UACR and estimated glomerular filtration rate.
After implementing the tool at the University of Virginia Health System, there were higher rates of testing for UACR in primary care encounters. The greatest impact was seen compared with a group that was not already using any automated reminders to increase screening.
"It is really important to make sure patients with type 2 diabetes are screened for CKD, but of course that isn't enough. The next steps that our team is working on is to make sure that CKD is recognized as a medical problem for the patient. Then a number of different tools may be able to assist clinicians with risk assessment and treatment," said corresponding author Margaret Spolnik, MD, of the Indiana University School of Medicine. "Ultimately, we want to promote evidence-based interventions like healthy lifestyle, risk factor control, and medications to reduce the risk of progressive CKD."
More information: Study: "Implementation of a Kidney Screening Intervention to Improve Early CKD Detection in Type 2 Diabetes (T2D)"
Provided by American Society of Nephrology