The development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is associated with a variety of genetic changes. Some of these alterations are epigenetic, wherein the sequence of the genes is unchanged, but chemical modifications to the DNA alter gene expression.
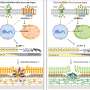
In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Daniel Tenen at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center found that a transcriptional regulator known as C/EBPG was highly expressed in a subset of AML samples that had an epigenetically silenced C/EBPA gene.
By blocking the epigenetic modification of C/EBPA, Tenen and colleagues found that they could reduce C/EBPG and restore normal myeloid blood cells.
This study suggests that targeting the balance of C/EBPG and C/EBPA could represent a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of AML.
More information:
C/EBPγ deregulation results in differentiation arrest in acute myeloid leukemia. Published in Volume 122, Issue 12 (December 3, 2012)
J Clin Invest. 2012;122(12):4490–4504. doi:10.1172/JCI65102
Abstract
C/EBPs are a family of transcription factors that regulate growth control and differentiation of various tissues. We found that C/EBPγ is highly upregulated in a subset of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) samples characterized by C/EBPα hypermethylation/silencing. Similarly, C/EBPγ was upregulated in murine hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells lacking C/EBPα, as C/EBPα mediates C/EBPγ suppression. Studies in myeloid cells demonstrated that CEBPG overexpression blocked neutrophilic differentiation. Further, downregulation of Cebpg in murine Cebpa-deficient stem/progenitor cells or in human CEBPA-silenced AML samples restored granulocytic differentiation. In addition, treatment of these leukemias with demethylating agents restored the C/EBPα-C/EBPγ balance and upregulated the expression of myeloid differentiation markers. Our results indicate that C/EBPγ mediates the myeloid differentiation arrest induced by C/EBPα deficiency and that targeting the C/EBPα-C/EBPγ axis rescues neutrophilic differentiation in this unique subset of AMLs.
Journal information: Journal of Clinical Investigation
Provided by Journal of Clinical Investigation