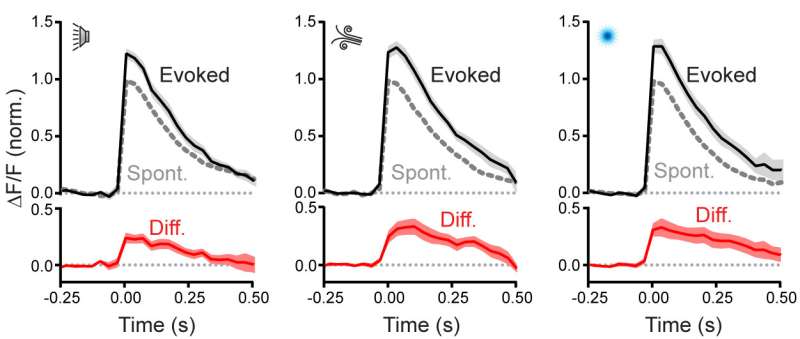
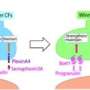
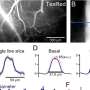
Average spontaneous and sensory-evoked calcium events across Climbing Fibers for different sensory modalities; the difference is shown in red. Sensory stimuli produced an enhancement of presynaptic signaling across sensory modalities. Credit: Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience
As we go about our daily lives, we are constantly bombarded by a steady stream of sensory information. Take a typical morning routine for example- roused from sleep by a shrill alarm, the strong aroma of freshly brewed coffee, and the brake lights and traffic horns of rush hour. In the course of a single day, we experience thousands of different cues across all senses.
Despite the numerous chaotic cues we encounter, our brains do a remarkable job assembling and processing them; allowing us to make sense of the world around us. This processing can take shape in very noticeable ways, such as our vision and hearing, but also occurs more subtly and unexpectedly. For instance, when learning a new movement, our brain is constantly keeping track of the sensory cues around us. This sensory snapshot helps to instruct and guide motor learning so that when we encounter the same context again, we'll be more likely to perform the movement in better way.
Though there is a wealth knowledge supporting the idea that sensory cues benefit motor learning, the precise brain circuitry and mechanisms tying these two together has been debated in recent years. Shedding new light on this topic, a recently published paper in Neuron from the lab of Dr. Jason Christie, Research Group Leader at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (MPFI), has revealed that a special input pathway into the cerebellum seems to hold the key to coding sensory information.
The cerebellum is a unique structure within the brain that plays a critically important role in motor coordination and learning that improves movements. By receiving many inputs from various regions of the brain, the cerebellum integrates and sends refined information out through a single neuron type called a Purkinje cell. One significant input to the Purkinje cells, are long-range projections called climbing fibers.
"Climbing fibers are very well-known and extensively studied in the field." describes Dr. Michael Gaffield, Research Fellow in the Christie Lab and first author of the publication. "These fibers form long-range connections with the cerebellum and are thought to deliver instructive motor signals and relay sensory information. But in the past few years it's been suggested that local circuits within the cerebellum, such as parallel fibers or molecular layer interneurons, may also play a part in coding of sensory information."
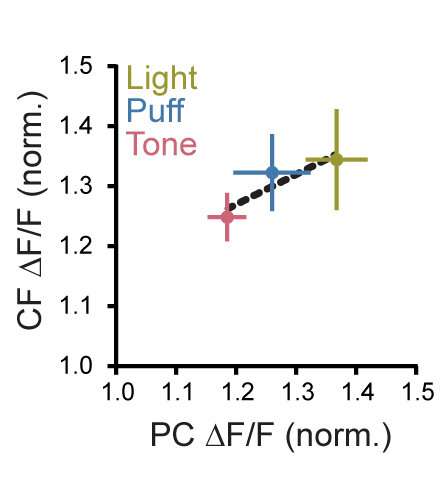
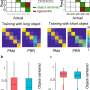
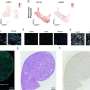
Comparison of the sensory enhancement of calcium event amplitudes in Climbing Fibers compared to observations in Purkinje cells, measured in separate experiments. The change in Purkinje cell response size closely parallels that of Climbing Fibers across modalities. Credit: Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience
To investigate, the team used two-photon calcium imaging to monitor the activity of Purkinje cells within the cerebellum of mice while presenting various sensory stimuli (auditory, visual and somatosensory). They then isolated and assessed changes in Purkinje cell activity that directly corresponded to the timing of each individual stimulus and climbing fiber input.
"Within each Purkinje cell, we saw a consistent enhancement of activity whenever a sensory stimulus was presented. But the enhancement wasn't the exact same across all three sensory types, it varied depending on the type of stimulus presented" explains Gaffield.
Next MPFI scientists examined if other cell types besides climbing fibers, contributed directly to the sensory enhanced activity seen in the Purkinje cells. Using the techniques of optogenetic inactivation (suppression of neural activity using light) and chemogenetic inhibition (suppression of neural activity using drugs), the team was able to inhibit individual cell types in the local cerebellar circuitry. Despite altering the local activity, no change occurred to the sensory enhanced activity of the Purkinje cells. However, by inhibiting climbing fiber activity directly, the enhancement was abolished; indicating that climbing fibers alone are responsible for conveying sensory information to the cerebellum.
Taking their investigation a step further, the Christie lab pioneered a novel technique allowing them to monitor the activity of climbing fiber axonal projections themselves. They discovered that when presenting sensory stimuli, the graded changes in the presynaptic activity of climbing fibers was accurately represented in the Purkinje cells; stronger activity in the climbing fiber was precisely mirrored by stronger activity in the Purkinje cells they connect with.
"Our results actually came as a bit of a surprise" notes Dr. Christie. "Traditionally it was thought that sensory signals arriving in the cerebellum were integrated and processed by Purkinje cells using local connections. Our findings demonstrate that Purkinje cells are merely reflecting what the climbing is doing. This means that a more distal region of the brain is doing the actual processing of sensory information and simply relaying it to the cerebellum. "
"Since Purkinje cell activity is critically important for motor learning, we are now in the process looking at sensory-derived activity during more complex motor behaviors" describes Dr. Christie. "Hopefully we will be able to uncover the neural mechanisms that underlie the climbing fiber's unique ability to convey sensory information and how learning benefits from this coding scheme."
More information: Conversion of Graded Presynaptic Climbing Fiber Activity into Graded Postsynaptic Ca2+ Signals by Purkinje Cell Dendrites, Michael A. Gaffield, Audrey Bonnan, and Jason M. Christie, Neuron, March 27 2019, Online Publication. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.010
Journal information: Neuron
Provided by Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience