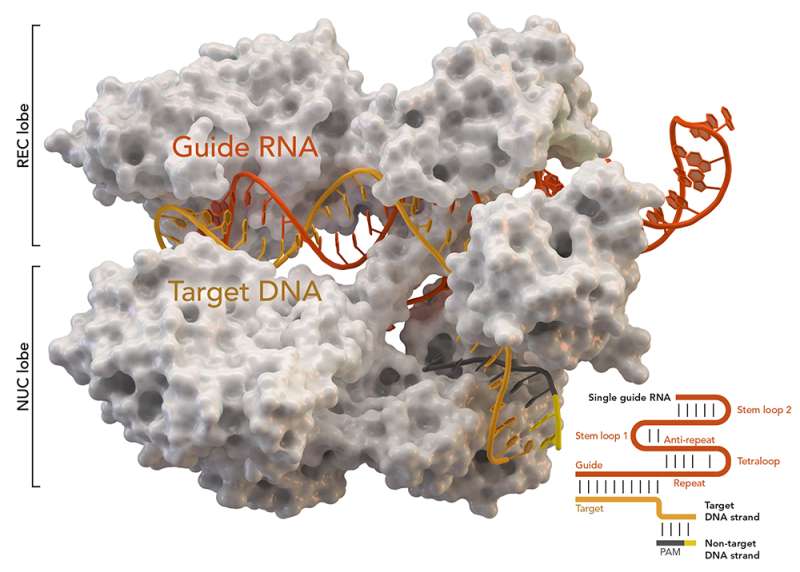
CRISPR-associated protein Cas9 (white) from Staphylococcus aureus based on Protein Database ID 5AXW. Credit: Thomas Splettstoesser (Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 4.0)
A group of researchers from the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Raras (CIBERER) (Biomedical Research Networking Centre on Rare Diseases), Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), the Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales y Tecnológicas (CIEMAT) (Research Center for Energy, Environmental and Technology), and the Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Fundación Jiménez Díaz (IIS-FJD) have led a study which demonstrates the viability of a gene editing strategy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (also known as butterfly children) with the tool CRISPR/Cas9 in preclinical models with this disease.
With this approach, published in the prestigious journal, Molecular Therapy, an unusually high number of patient cells have been corrected (more than 80 percent) obtaining two of the properties sought after when developing new therapies: biological safety and therapeutic efficiency. "This work enables us to establish the basis for a rapid transfer to clinical trials," explained Marcela del Río, the study's coauthor and Professor at the UC3M Department of Bioengineering.
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, an aggressive subtype of epidermolysis bullosa, is a rare disease resulting in severe skin fragility, characterized by the continuous formation of erosions and blisters on the skin and internal mucous membranes, as well as fibrosis and diverse complications such as pseudo-syndactyly (fusion of the fingers) and an elevated risk of developing metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dealing with this disease represents a challenge for health professionals and a great effort on the part of patients and their families.
This disease, of a genetic origin, is caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, which codifies for type VII collagen (C7), a protein essential for dermo-epidermal adhesion. In Spain, there is a high prevalence of one of these mutations, located at exon 80 of the gene (present in approximately 50 percent of the cohort of Spanish patients), which justifies the development of a precision therapy targeting this region of the gene.
Gene editing with CRISPR/Cas9
The authors of this study have applied the gene-editing tool CRISPR/Cas9, which in this case is employed to safely and accurately eliminate from the stem cells of the skin of patients the exon 80 of the COL7A1 gene, which contains the pathogenic mutation. This leads to the production, from the edited cells, of a functional C7 variant.
Transplantation of a bioengineered skin equivalent carrying patients' cells "cured" using this new technology has shown to be capable of regenerating completely normal tissue in a reliable preclinical model of the disease.
Until now, the molecular tool CRISPR/Cas9 lacked the necessary levels of efficiency for realistic clinical applications using adult stem cells, such as hematopoietic or skin (epidermal) stem cells. Therefore, these strategies could not compete with conventional gene addition therapy using viral vectors. "However, this study showed that the new non-viral gene edition approach developed was even more effective than viral gene addition therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa," the study's coauthor, Fernando Larcher, from CIEMAT, pointed out. In addition to its effectiveness, the strategy turned out to be safe by virtue of the absence of undesirable effects on the rest of the patient genome.
More information: Jose Bonafont et al. Clinically Relevant Correction of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa by Dual sgRNA CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing, Molecular Therapy (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.03.007
Journal information: Molecular Therapy
Provided by Carlos III University of Madrid