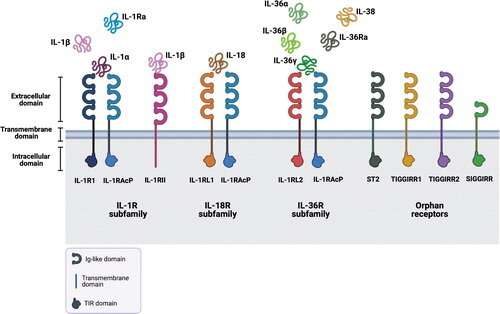
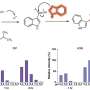
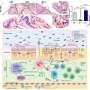
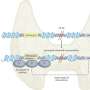
FIG. 1. Molecular structure of the IL-1 receptor family. Modified from Martin and Wesche (2002). IL, interleukin. Created with BioRender.com. Credit: DOI: 10.1089/jir.2021.0173
The Interleukin-1 Receptor-Like 2 (IL-1RL2) cytokine can promote inflammatory diseases and have a role in controlling infection. The receptor can recognize multiple agonists and has been implicated in the development of inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A comprehensive review of IL-1RL2 is published in the Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR).
O. Medina-Contreras, from Mexico Children's Hospital, and coauthors, review the many implications of IL-11RL-2, also known as IL-36 in the skin, lungs, and gut. They discuss its ability to promote the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and its role in infection, including a potential role in COVID-19 pathology.
"It seems that the IL-36IL-1RL2 axis has both inflammatory and healing functions, probably depending on other mediators in the extracellular milieu and the stage of the infection," state the investigators. "There is still much to discover about this recently described cytokine family, its functions in other organs, and how it accomplishes a dual effect in both inflammation and healing."
"This is a fascinating review that highlights the importance of IL-36-IL-1RL2 in the development of several inflammation-related diseases and the healing process. The paper is an excellent example of the innovative and cutting-edge research published in the journal," says Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research Editor-in-Chief David L. (Woody) Woodland, Ph.D.
More information: Laura D. Manzanares-Meza et al, Interleukin-1 Receptor-Like 2: One Receptor, Three Agonists, and Many Implications, Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (2022). DOI: 10.1089/jir.2021.0173
Provided by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc