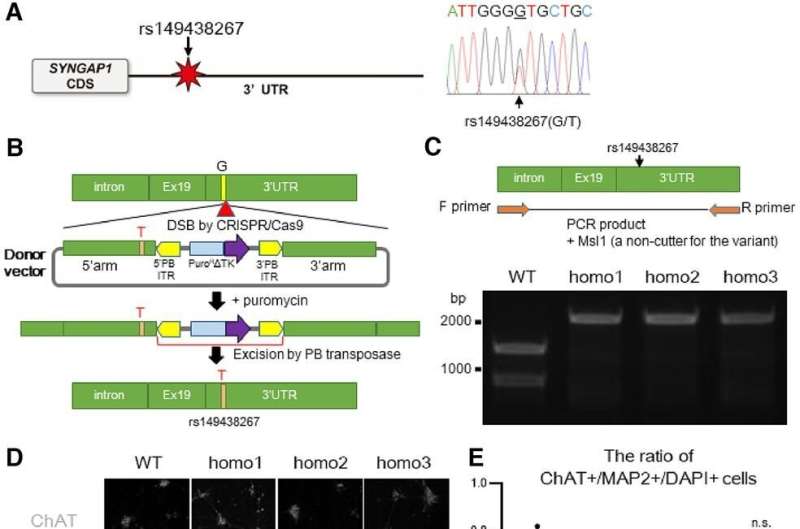
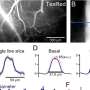
Motor neurons with the SYNGAP1 rs149438267 homozygous mutation exhibit a loss of dendritic spines. A, The location of the SYNGAP1 variant rs149438267 (g.33452118G>T, c.*212G>T, GRCh38.p12; left). Sanger sequence of a patient with the SYNGAP1 3′UTR variant rs149438267 (right). Genomic DNA were extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes, and the heterozygous variant g.33452118G>T was confirmed. B, A schematic overview showing the strategy for scarless genome editing, inserting rs149438267 into iPSCs (201B7). C, RT-PCR was performed using primer sets to amplify DNA extracted from wild-type and edited homozygous iPSCs. PCR products were digested by Msl1, a noncutter for the SYNGAP1 mutation, and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. D, iPSC-derived motor neurons with the wild-type or homozygous mutation were cultured for four weeks and were immunostained for MAP2 (red), ChAT (white), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. E, Quantification of the ratio of ChAT/MAP2/DAPI-positive cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM n = 9 fields, each from 3 independent wells; n.s., not significant, Kruskal–Wallis test, Bonferroni post hoc test. F, iPSC-derived motor neurons were immunostained for F-actin (green), MAP2 (red), and ChAT (white). Scale bars: 20 µm for left columns, 10 µm for right columns. G, Quantification of the number of spines per 20 µm of dendrite length. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM n = 18 each; ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test. Credit: The Journal of Neuroscience (2022). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0455-22.2022
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have identified a novel genetic variant found in some patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Employing human-induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, they detailed the process by which this variant relates to ALS. The investigators expect this mechanism to be a new therapeutic target for ALS treatment. The findings are reported in the Journal of Neuroscience.
ALS is a progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disease where a person gradually loses motor neurons and has muscle weakness. The mechanisms and causes of this disease are not well understood and there is no treatment. Furthermore, ALS is a diverse disease; different patients seem to have different causes, mechanisms, and symptoms. Researchers know that a protein called Fused-in sarcoma (FUS) plays a key role in the disease. Ordinarily, FUS binds to RNA and regulates functions of RNA. On the other hand, FUS dysfunctions are associated with various neurodegenerative diseases, including ALS.
Dr. Satoshi Yokoi and his colleagues in the Department of Neurology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, have been studying this FUS protein. Previously, they found that the FUS protein interacted with RNA that encodes a protein called SYNGAP1. SYNGAP1 helps with synaptic formation, which is essential for neurons to work together. "Currently, no study has reported that SYNGAP1 is involved in the mechanism of ALS. However, given its close relationship with FUS, we wanted to investigate whether SYNGAP1 has anything to do with ALS," said Dr. Yokoi, a lead author of the study.
First, the team searched for a variant of the SYNGAP1 gene in patients with ALS. They found seven out of 807 patients who had the variant. Next, to examine the behavior of the SYNGAP1 variant, they replicated this variant gene in human iPS-derived motor neurons.
An iPS cell is a type of stem cell that scientists can transform into any type of cell in the body, including neurons. It is especially useful in medical research because researchers can generate, for example, diseased cells and conduct different tests on them in a living state.
This contrasts with traditional methods in which researchers conduct tests on animal cells or outside of a living organism.
In this study, the researchers generated motor neurons with the SYNGAP1 variant from iPS cells. In these neurons, researchers observed several abnormal behaviors compared to normal motor neurons. Especially, the variant excessively recruited the FUS protein, as well as to another RNA-binding protein called HNRNPK. This excessive binding inhibited synaptic formation.
In particular, excessive recruitment of HNRNPK, rather than FUS, seemed to be a primary cause of synaptic dysfunction with the SYNGAP1 variant. Furthermore, when researchers applied antisense RNA that blocks the excessive binding of HNRNPK to SYNGAP1 RNA, they recovered synaptic formation, meaning that motor neurons can work together. This indicates that, in the future, scientists could utilize antisense RNA to develop ALS drugs.
Excessive binding of HNRNPK to SYNGAP1 was causing synaptic abnormality, which explains the process of early-stage ALS when synapse loss takes place. Additionally, while previous ALS research focused on FUS, this study underscored the crucial roles of SYNGAP1 and HNRNPK. The antisense RNA used in the current research is only effective for those patients with the variant SYNGAP1. Nonetheless, the researchers hope that the discovery of this new mechanism can provide new insight into other types of ALS.
Interestingly, this study also found that SYNGAP1 behaved differently in human iPS cells compared to the mouse model, which had been used for SYNGAP1 research. "We believe that using human-derived samples is crucial so that the observations from these cells directly apply to patients," said Dr. Yokoi.
Although the researchers described one mechanism of ALS, much remains to be investigated because ALS involves multiple different mechanisms and causes. "The ALS patients I see in my daily practice have yet to receive curative treatment. We will continue research to find something that can apply to future ALS treatments," said Dr. Yokoi.
More information: Satoshi Yokoi et al, TheSYNGAP13'UTR variant in ALS patients causes aberrantSYNGAP1splicing and dendritic spine loss by recruiting HNRNPK, The Journal of Neuroscience (2022). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0455-22.2022
Journal information: Journal of Neuroscience
Provided by Nagoya University