Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain
A new editorial paper titled "Obesity paradox and lung cancer, metformin-based therapeutic opportunity?" has been published in Oncotarget.
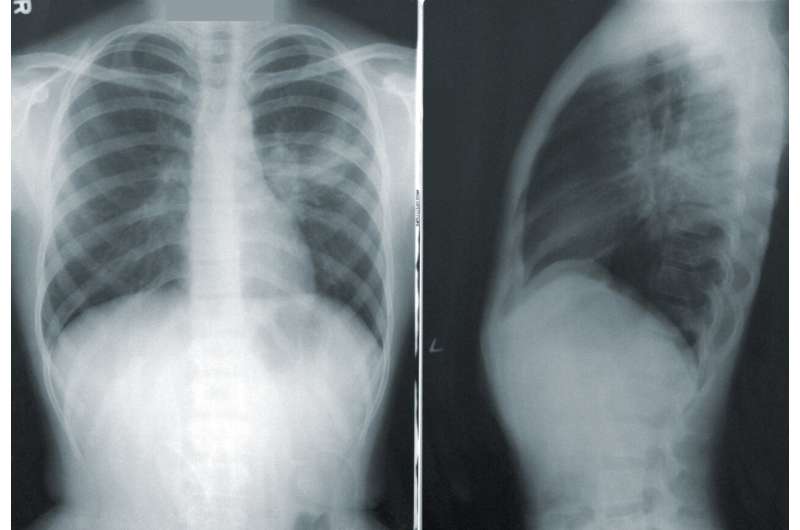
In their recent editorial, researchers Pedro Barrios-Bernal, Norma Hernández-Pedro, Luis Lara-Mejía, and Oscar Arrieta from Instituto Nacional de Cancerología discuss obesity, diabetes and lung cancer. Obesity is a complex multifactorial disease with detrimental effects on health. This disease induces a proinflammatory state, innate and adaptative immune system dysfunction, and immune exhaustion, which in conjunction promote cancer growth.
Although obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have been associated with lung cancer (LC) development, several confounding factors, such as chronic inflammation, high insulin levels, microbiome, as well as the oncogenic potential of growth and sexual hormones, have introduced uncertainty and avoid the full recognition of this relationship. Thus, therapies that can bring potential therapeutic effects to both comorbidities are being tested globally and their effect on cancer cells.
"Altogether, there is a strong relationship between high BMI and increase survival in different LC stages and in combination with some anticancer therapies. Metformin has been shown to be a metabolism modifier that may adapt signaling pathways and immune sensitivity in tumor microenvironment," the paper states.
More information: Pedro Barrios-Bernal et al, Obesity paradox and lung cancer, metformin-based therapeutic opportunity?, Oncotarget (2023). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28432
Provided by Impact Journals LLC