Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute have discovered a mechanism that causes long-term memory loss due to age in Drosophila, the common fruit fly, a widely recognized substitute for human memory studies.
Everyone worries about losing their memory as they grow older—memory loss remains one of the most common complaints of the elderly. But the molecular reasons behind the processes remain unclear, particularly those associated with advancing age.
Now, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have discovered a mechanism that causes long-term memory loss due to age in Drosophila, the common fruit fly, a widely recognized substitute for human memory studies.
The new study, published recently in The Journal of Neuroscience, describes in detail the loss of connectivity between two sets of neurons that prevents the formation of long-term memory.
"We show how long-term memory is impaired with age in Drosophila," said Ron Davis, a TSRI professor and chair of the Department of Neuroscience who led the study. "This isn't due to any functional defects, but to connectivity problems between neurons."
The most widely studied form of memory in fruit flies is memory of smell. When an odor is paired with a mild electric shock, the flies develop short-term memories that persist for around a half-hour, intermediate-term memory that lasts a few hours and long-term memory that persists for days.
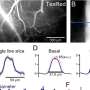
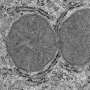
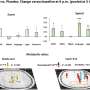
Using real-time cellular imaging to monitor the changes in aged flies' neuron activity before and after learning, Davis and his colleague Ayako Tonoki found structural connectivity defects between a set of neurons known as dorsal paired medial neurons and mushroom body neurons; these defects prevented long-term memories from forming.
Long-term memories require new synapses and new proteins to be formed—as compared to short-term memory, which is built from existing proteins.
"Now that we know long-term memory loss is a connection problem," said Davis, "to improve memory we're going to have to think of ways of rebuilding those connections."
More information: The Journal of Neuroscience, January 21, 2015. 35(3):1173–1180
Journal information: Journal of Neuroscience
Provided by The Scripps Research Institute