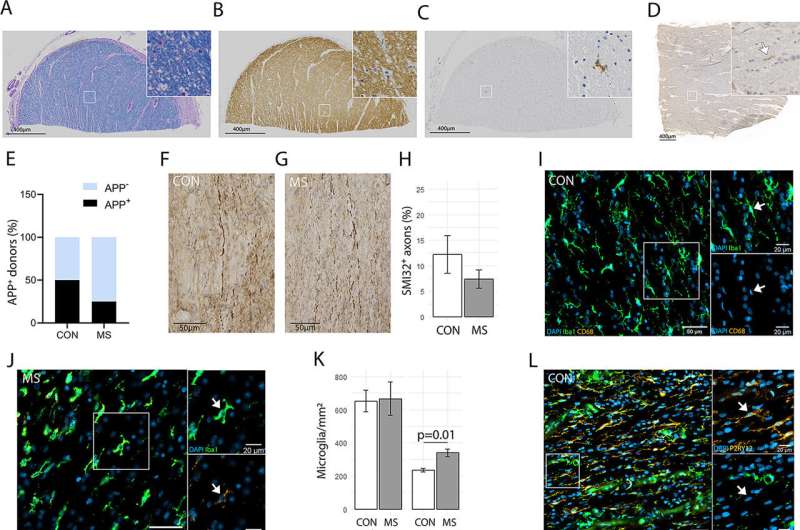
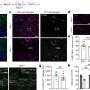
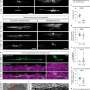
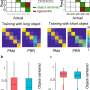
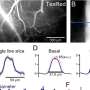
Inflammation occurring in the normal-appearing white matter. (A) Luxol Fast Blue, (B) proteolipid protein, and (C) Kim1p stainings of the optic nerve shows no demyelination or reactive sites, other than from some nodules, with a scale bar of 400nm. (D) Amyloid precursor protein (APP)+ axonal fragments (E) were found in both control (CON) and multiple sclerosis (MS) tissue. (F) Nonphosphorylated neurofilament H (SMI32)+ axons were observed in both and (G) MS tissue, and (H) the percentage of tissue that was SMI32+ was comparable in control and MS tissue. (I) Iba1 (in green) and CD68 (in yellow) staining of a control optic nerve with enlarged panels with arrows pointing to an Iba1+CD68− cell. (J) Iba1 (in green) and CD68 (in yellow) staining of an MS optic nerve with enlarged panels with arrows pointing to an Iba1+CD68+ cell. (K) In MS compared to controls, there are an equal amount of Iba1+ microglia/mm2 and more Iba1+CD68+ microglia/mm2 (p = 0.01). (L) Human leukocyte antigen (HLA; in green) and P2RY12 (in yellow) staining of control optic nerve with 2 enlarged panels, in the first panel an arrow pointing to a P2RY12+HLA− cell and in the second panel an arrow pointing to a P2RY12+HLA+ cell. (M) HLA (in green) and P2RY12 (in yellow) staining of MS optic nerve with 2 enlarged panels, in the first panel an arrow pointing to a P2RY12+HLA+ cell and in the second panel an arrow pointing to a P2RY12−HLA+ cell. (N) In MS compared to controls, there are equal numbers of P2RY12+HLA− and P2RY12+HLA+ microglia/mm2 and more P2RY12−HLA+ microglia/mm2 (p = 0.04). (O) CD3 (in yellow) staining of control optic nerve and (P) CD3 (in yellow) staining of MS optic nerve with arrows pointing to CD3+ T cells. (Q) In MS compared to controls, there are more CD3+ T cells/mm2 (p = 0.04). (R) As assessed with laminin (in green), CD3+ T cells (in yellow) were found both in the perivascular space and in the parenchyma, and (S) the percentage of CD3+ T cells in the parenchyma was similar in MS compared to controls. DAPI = 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Credit: Annals of Neurology (2022). DOI: 10.1002/ana.26585
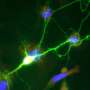
It is 7 am, the alarm clock rings—you open your eyes, swing your legs out of bed, give a talk at work, play a tennis match in the evening. Billions of nerve cells that make up the gray matter in our brain allow us to perform these different tasks. They are interconnected millions of times by nerve fibers running deeper in the brain, called axons. Many of these axons are wrapped by a cellular "insulating tape."
The insulating cover is made of myelin, a lipid-rich substance that coats axons in up to 150 layers. Together, axons and myelin form what is known as white matter. At regular intervals, the myelin sheaths have a small gap called a node of Ranvier. When a signal is transmitted from one cell to the other by means of an electrical nerve impulse, it literally jumps from one node to the next. This accelerates communication on myelinated axons by 100 times.
The white matter, however, is more than a well-sorted and optimally insulated "cable collection." It helps with various different processes in the brain, such as learning, memory, or social skills. If this tissue is damaged, diseases such as MS can develop. In MS, which affects up to 280,000 people in Germany alone, the myelin layer around the axons is damaged or destroyed. These lesions, combined with inflammatory reactions, can be detected by imaging techniques.
However, scientists still know little about how changes in axons and myelin at the subcellular level are related to inflammatory processes. Researchers led by Wiebke Möbius at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen and Inge Huitinga at the Netherlands Institute for Neurosciences in Amsterdam (the Netherlands) have now discovered that the fine structure—called ultrastructure—of the seemingly normal white matter in MS patients is already altered, before the first foci of inflammation appear. Their research is published in the journal Annals of Neurology.
Quality of myelin samples decisive
"The areas that may be critical for MS disease can only be studied at the ultrastructural level using electron microscopy," Möbius says. However, she adds, the tissue structures are often damaged in conventional preparation methods due to chemical fixation and embedding.
"This is especially true for the sensitive myelin. The big challenge for us, therefore, was to preserve the structures in the tissue sample better than before. To do this, we optimized the fixation method of the samples in particular," explains the head of the Facility for Electron Microscopy at the MPI's City Campus.
For their experiments, the scientists used tissue samples from the Netherlands Brain Bank. These came from MS patients who had agreed during their lifetime to donate their brains post-mortem for research and medical records.
As the team showed, in the normal appearing white matter of MS patients, the myelin sheaths are conspicuously altered and the myelin is less compact. The nodes of Ranvier are also disorganized. In addition to these structural changes, the researchers found cellular markers for inflammation in the apparently normal tissue: T lymphocytes and activated immune cells of the brain called microglial cells.
Last but not least, the density of mitochondria—the power generators of the cell—was strikingly increased in the processes of nerve cells, suggesting that communication between nerve cells requires more energy than in healthy people. Aletta van den Bosch from the Dutch group explains: "Mitochondria not only produce vital energy, but also many by-products such as oxygen radicals. We suspect that these may increase myelin damage."
Möbius adds, "We can see clearly that in MS, ultrastructural changes in the white matter are related to chronic inflammation in the brain. Both pathological abnormalities could contribute to the progression of the disease. The fact that the ultrastructure of myelin can now be preserved in such quality for studies under the electron microscope will hopefully provide further new insights."
More information: Aletta M. R. van den Bosch et al, Ultrastructural Axon–Myelin Unit Alterations in Multiple Sclerosis Correlate with Inflammation, Annals of Neurology (2022). DOI: 10.1002/ana.26585
Journal information: Annals of Neurology
Provided by Max Planck Society