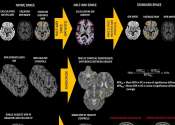
DeepWMH: A deep learning tool for accurate white matter hyperintensity segmentation
White matter hyperintensities (WMHs) on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images are imaging features in various neurological diseases and essential markers for clinical impairment and disease progression. WMHs ...
Apr 22, 2024
0
1