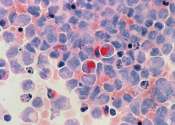
Alarming rise found in esophageal cancer and Barrett's esophagus in middle-aged adults
Adults aged 45 to 64 experienced a nearly doubled rate of esophageal cancer and a 50 percent increase in the precancerous condition Barrett's esophagus between 2012 and 2019, according to a database analysis of roughly five ...
May 13, 2022
0
100