Impressions shaped by facial appearance foster biased decisions
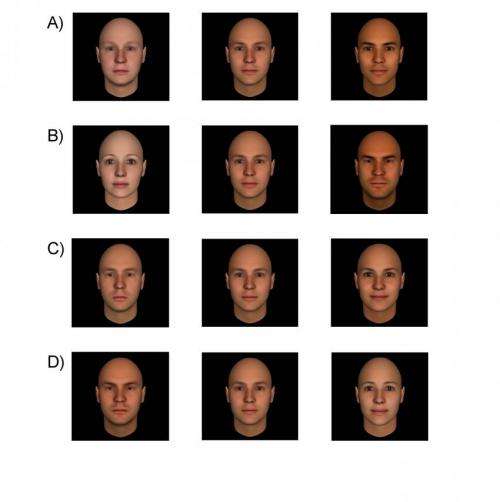
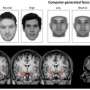
Research in recent years has shown that people associate specific facial traits with an individual's personality. For instance, people consistently rate faces that appear more feminine or that naturally appear happy as looking more trustworthy. In addition to trustworthiness, people also consistently associate competence, dominance, and friendliness with specific facial traits. According to an article published by Cell Press on October 21st in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, people rely on these subtle and arbitrary facial traits to make important decisions, from voting for a political candidate to convicting a suspect for a crime. Referring to this systemic bias as "face-ism," the authors present its real-world consequences and discuss potential ways of overcoming it.
"Although we would like to think our judgments and choices are rational, impartial, consistent, and solely based on relevant information, the truth is that they are often biased by superficial and irrelevant factors," says Christopher Olivola of Carnegie Mellon University's Tepper School of Business, lead author of the review article, which he co-authored with Princeton University researchers Friederike Funk and Alexander Todorov. "This is a troubling human tendency that needs to be corrected, or at least mitigated, because faces are not valid predictors of a person's traits."
Numerous studies have shown that people form impressions of aspiring leaders based on their faces, and that these superficial impressions predict important social outcomes. For example, political candidates with naturally competent-looking faces are more likely to win elections than those who look incompetent, and having a naturally dominant-looking face predicts rank attainment in the military.
The bias to rely on facial appearance to make decisions can also lead to serious consequences in the legal system and financial realm. People are more likely to convict individuals whose faces look untrustworthy or guilty, while having a face that looks trustworthy strengthens an individual's ability to attract financial investments and procure loans.
Uncovering the facial variations that lead to impressions of competence or trustworthiness is still an active area of research. Although much remains unknown, recent methodological advances, such as sophisticated computer-based models that systematically manipulate facial appearance, are allowing researchers to tackle this question with unprecedented rigor.
Although face-ism is widespread, research suggests that it could be reduced by arming people with more relevant and valid types of information. For instance, knowing more about a political candidate and his or her positions or past behavior makes voters less likely to be influenced by facial traits. "We need to guard against letting our choices be biased by superficial cues," Olivola says. "In some contexts, educating people might be sufficient to reduce facial stereotyping. In other contexts, however, more research will be needed to identify the best way to mitigate the biasing influence of facial appearance."
More information: Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Olivola et al. "Social attributions from faces bias human choices"