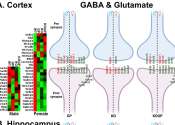
Making long-term memories requires DNA damage, researchers discover
Just as you can't make an omelet without breaking eggs, scientists at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found that you can't make long-term memories without DNA damage and brain inflammation. Their surprising findings ...
Mar 27, 2024
1
532