Hospital rankings dramatically affected by calculation methods for readmissions and early deaths
Hospital readmission rates and early death rates are used to rank hospital performance but there can be significant variation in their values, depending on how they are calculated, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"Hospital-specific readmission rates have been reported as a quality of care indicator but no consensus exists on how these should be calculated. Our results highlight that caution is required when comparing hospital performance based on 30-day or urgent readmissions given their notable variation when methods used in their calculation change," says Dr. Carl van Walraven, lead author of the study, scientist at ICES@uOttawa, senior scientist at Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (OHRI) and associate professor at the University of Ottawa (uOttawa).
Hospital readmission rates are often used as an indicator of quality of care. However the use of different methods and variables can result in different outcomes, as this study indicates.
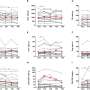
The study calculated hospital-specific 30-day death or readmission rates for adults at all 162 Ontario hospitals between 2005 and 2010 using different methods for confounder adjustment (age-sex v. complete) and different units of analysis (all hospitalizations v. 1 per patient).
- Hospital-specific rankings varied extensively—ranking changed based on which methodology was used.
- Readmission rates adjusted for age-sex alone had the greatest variation.
- Notable variation in 30-day death or urgent readmission rates based on how they were calculated.
- Slight changes in the methods used to calculate hospital-specific readmission rates have a large influence on their values and the consequent hospital rankings.
"Our results highlight the caution required when comparing hospital performance using rates of death or readmission within 30 days," writes van Walraven with coauthors. "To measure quality of care, one would ideally measure the number of avoidable readmissions."
The authors recommend caution in using this measure to compare hospital performance.
"We found that slight changes in the methods used to calculate hospital-specific readmission rates had large influences on their values and the consequent hospital rankings. This should be kept in mind when comparing hospital performance using readmission rates," says van Walraven.
More information: www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.120801