Gonorrhoea and syphilis in Norway in 2014
Reported cases of gonorrhea continue to increase in Norway, both among men who have sex with men (MSM) and among heterosexuals. The increase of gonorrhea among heterosexual women was particularly significant. Reported cases of syphilis in 2014 remained at the same high level as in 2013. It has been 25 years since so many cases of these infections have been registered in Norway.
The transmission pattern of gonorrhea and syphilis among MSM largely follows the infection pattern of HIV. Most MSM are infected during casual sex in Oslo, but there is a tendency for more MSM to be infected in the rest of Norway, especially in larger cities like Bergen, Trondheim and Stavanger, or on trips to European cities. Most are infected at casual sex venues. Sexually active MSM should be offered regular examinations and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The increased number of reported cases of gonorrhoea and syphilis among heterosexuals observed in 2014 should alert the health services that these diseases are no longer uncommon. Gonococci are highly infectious and the outbreak potential is significant if the microbe is introduced in casual sex settings. The increased incidence among women could provide challenges in connection with pregnancy and birth.
Gonorrhoea
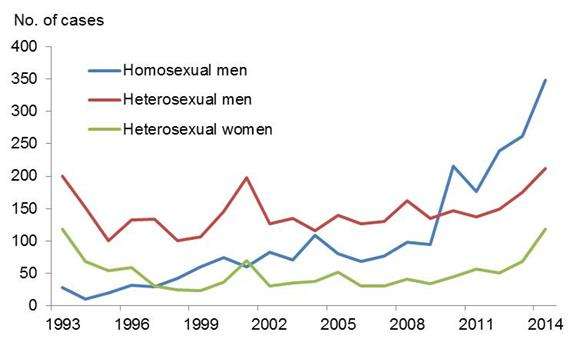
In 2014, there were 682 gonorrhoea cases diagnosed in Norway, compared with 506 cases in 2013. The significant increase in gonorrhoea among MSM that began in 2010 continued in 2013. In 2014, there was a considerable increase in reported cases among heterosexual men and women compared with 2013 (figure 1). Of the 682 cases, 563 were men and 119 were women. Of the men, 347 men were infected homosexually, 212 were infected heterosexually and four men had an unknown sexual orientation. The increase of gonorrhoea in 2014 was seen mainly in Oslo, but the counties Rogaland and Sør-Trøndelag also saw a significant increase, both among homosexuals and heterosexuals. The increase in reported cases in recent years is largely due to a combination of increased use of PCR in diagnosis and a real increase in the incidence of the disease.
Syphilis
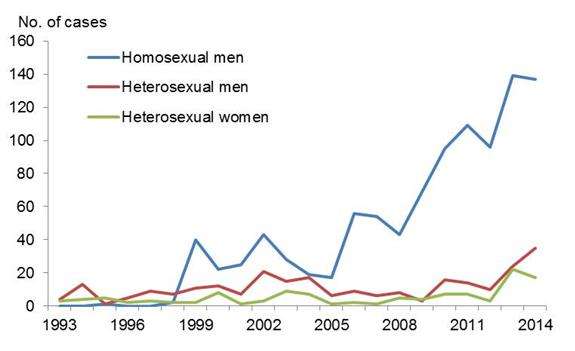
In 2014, there were 189 diagnosed cases of primary, secondary or early latent syphilis compared to 185 cases in 2013. Of the reported cases, 137 men (72 per cent) were infected homosexually (139 cases in 2013) and 52 were infected heterosexually (46 cases in 2013).
In 2013, the number of reported cases of syphilis in Norway increased significantly among both MSM and heterosexually-infected men and women, and in 2014, the number of reported cases remained at a high level (figure 2).
Of the 189 cases reported in 2014 there were 172 men and 17 women. Of the 2014 cases, 52 per cent came from Oslo whilst the significant increase of reported cases in Hordaland county was due to increased transmission among MSM (20 cases in 2014). 77 per cent of the 189 cases of syphilis reported in 2014 were born in Norway.