Anti-epileptic drug linked to birth defects when taken with other drugs
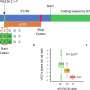
In an analysis of pregnancies in Australia from 1999 to 2014 in which women were taking anti-epileptic drugs, fetal malformation rates fell over time in pregnancies where only one drug was taken, but rates increased in pregnancies where multiple drugs were taken.
The rise in such "polytherapy" malformation rates began around 2005 when levetiracetam and topiramate use began to increase. Malformation rates were similar in polytherapy pregnancies whether or not levetiracetam was included (7.14 percent versus 8.38 percent), but were higher in polytherapy pregnancies involving topiramate (14.94 percent versus 6.55 percent).
The findings suggest that use of topiramate in conjunction with other anti-epileptic drugs may enhance its propensity to cause fetal malformations. The mechanisms involved are currently unclear.
"Although the results are based on small numbers of patients in pregnancy, we suggest that the use of topiramate, at least in combination with other anti-epileptic medications, ought to be used with caution in women who plan to become pregnant," said Dr. Frank Vajda, lead author of the Epilepsia analysis.
More information: Frank J. E. Vajda et al, Antiepileptic drug combinations not involving valproate and the risk of fetal malformations, Epilepsia (2016). DOI: 10.1111/epi.13415