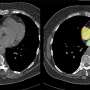
Smartwatch effective in detecting atrial fibrillation
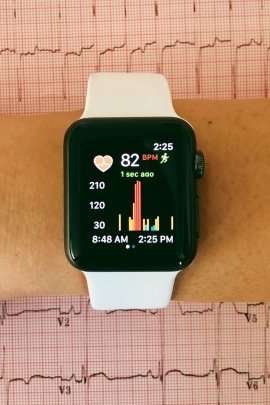
Irregular heart impulses that lead to stroke can be detected with great accuracy using a smartwatch with a specially designed application, a finding that could eventually lead to new ways to screen patients for earlier treatment, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
The peer-reviewed study, which used an app specifically designed for the Apple Watch, is believed to be the first on utilizing a smartwatch to detect atrial fibrillation (AF) or any arrhythmia. Findings appear online March 21, 2018, in JAMA Cardiology.
"Given the broad and growing use of smartwatches and ready accessibility of downloadable mobile applications, this approach may ultimately be applied to efficiently screen for AF," said senior author Gregory Marcus, MD, MAS, a UCSF Health cardiologist and director of clinical research in the UCSF Division of Cardiology. "By identifying candidates for appropriate anticoagulation treatment, we might ultimately leverage common wearable devices to reduce major thromboembolic complications, even death."
In AF, electrical impulses in the upper chambers of the heart are chaotic, and the atrial walls quiver rather than contracting normally in moving blood to the lower chambers. As a result, blood clots may form. One in four adults over age 40 is at risk for AF, with a projection of nearly 6 million people in the nation having the condition by 2050.
One of the leading causes of stroke, AF is often without symptoms and can remain undetected until a stroke actually occurs. Earlier detection would enable the use of anticoagulation therapy to mitigate the risk of stroke and other complications such as dementia, chronic kidney disease and heart attack.
AF patients can use wireless devices on the market to track their heart rate. However, because they are not meant to be worn all the time, they inevitably miss some data.
The popularity of the Apple Watch, along with its high-quality heart-rate sensor, makes it an attractive tool for large-scale AF screening, said Marcus, holder of the Endowed Professorship of AF research in the UCSF School of Medicine. When coupled with deep neural networks – a type of machine-learning algorithm that has demonstrated high accuracy in performing pattern and image recognition – the devices would be able to provide continuous data collection to detect irregular heart rhythms.
In the JAMA Cardiology study, Marcus and his colleagues assessed data from three sets of participants, starting with a remote group of 9,750 participants in the UCSF Health eHeart Study. This group, which included 347 people with known AF, used the Apple Watch and an app developed by Cardiogram, Inc., to provide more than 139 million measurements of heart rates and step counts in workout mode to train the app's deep neural network. A subset of these patients used an AliveCor smartphone device equipped with electrodes to obtain a single electrocardiogram (ECG) to help train the algorithm.
The resulting Cardiogram data then was validated against a group of 51 UCSF patients with AF undergoing a cardioversion procedure, which electrically shocks the heart back into normal rhythm, as well as against a second validation group of 1,617 Health eHeart participants (64 with AF) using the Apple Watch.
When compared to the cardioversion cohort, the researchers found the Cardiogram algorithm was 97 percent accurate, while the two standard statistical methods for AF detection were 91 percent and 86 percent accurate. It also was nearly twice as accurate as the two standard methods in predicting AF in the second validation group, which only used the Apple Watch, at 72 percent versus 48 percent and 45 percent.
"We also learned from this study that a novel method can be utilized to train a deep neural network using less data while still achieving high accuracy," said study co-lead author Geoffrey Tison, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine. "This is especially relevant when applying deep neural networks to medical tasks where the disease-specific data is often costly to label with a gold standard and where the datasets are relatively small in sample size compared to those for deep learning applications in other fields."
The JAMA Cardiology study confirms a preliminary presentation by Marcus and his colleagues at the annual Heart Rhythm Society conference in May 2017 that showed the algorithm flagged AF episodes with 97 percent accuracy.
Among the study limitations, Apple Watch was the only smartwatch used, so similar devices may not be as effective. The researchers noted possible selection bias, as a number of participants contacted for the study did not complete initial surveys and link Cardiogram accounts. All patients also either owned a smartwatch or, for the cardioversion cohort, had a coordinator to assist with device setup, so results may not generalize to less "tech-savvy" individuals. As data focused on those with known AF, researchers did not show the ability to identify a new diagnosis of the disease.
More information: Geoffrey H. Tison et al. Passive Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Commercially Available Smartwatch, JAMA Cardiology (2018). DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.0136