Amblyopia linked to lower self-perception in children
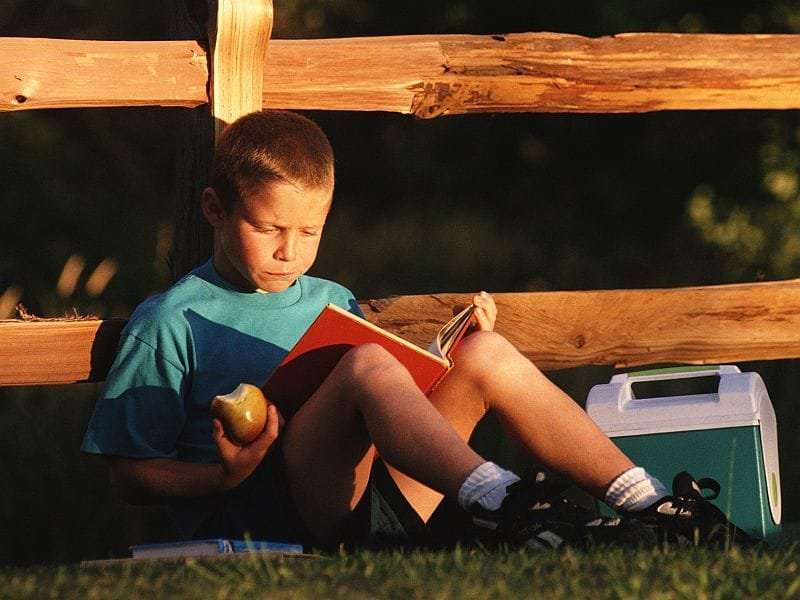

(HealthDay)—Children with amblyopia report lower self-perception for scholastic, social, and athletic measures, which may be associated with slower reading speed and worse motor skills, according to a study published online Nov. 15 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Eileen E. Birch, Ph.D., from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues surveyed healthy children in grades three to eight regarding self-perception of competence, appearance, conduct, and global self-worth. Participants included 50 children with amblyopia; 13 children without amblyopia with strabismus, anisometropia, or both; and 18 control children.
The researchers found that children with amblyopia had significantly lower scores than control children on the scholastic, social, and athletic competence domains of the Self-Perception Profile for Children. Further, a lower self-perception of scholastic competence was associated with a slower reading speed, and a lower self-perception of scholastic, social, and athletic competence was associated with worse performance of aiming and catching among children with amblyopia. There were no significant differences between the groups regarding the self-perception of physical appearance or global self-worth.
"These results suggest lower self-perception and its association with reading speed and motor skills highlight the potentially wide-ranging influence of altered visual development in children in their everyday lives," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Editorial (subscription or payment may be required
Copyright © 2018 HealthDay. All rights reserved.