Study finds 'cluster of disadvantage' behind BAME psychosis rates
Excess psychosis diagnoses amongst Black and South Asian men in deprived urban areas could reflect a cluster of disadvantage in specific places, rather than individual experiences of deprivation alone, a study led by Queen Mary University of London researchers concludes.
The paper, published today in the British Journal of Psychiatry, is the first to apply a syndemic approach to psychiatry.
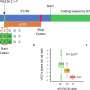
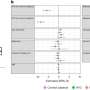
The team compared the incidence of several health conditions—including psychosis—between White, Black and South Asian men across Britain. They also studied data for an additional group of men from the deprived inner-London borough of Hackney. Although levels of diagnosed psychosis were significantly higher amongst black and south Asian men across Britain than for white men, the gap disappeared after taking account of socio-economic factors such as social class and unemployment.
However, after allowing for those factors the team found a significant gap remained in diagnosed levels of psychosis and other health conditions amongst Black and South Asian men living in Hackney. This could be explained, they suggest, by four markers of vulnerability that could reinforce each other and aggravate the risk of developing severe mental illness.
The components of the syndemic were drug and alcohol dependence, criminality and violence, risky or coercive sexual behaviour and psychosis/anxiety.
Diagnosed levels of psychosis and anxiety were much more severe among men in Hackney who engaged in such behaviours.
After factoring in these markers, diagnosis rates closely matched those for their ethnic counterparts across Britain—and for White men in Hackney.
Co-author Professor Kam Bhui, Head of Queen Mary's Centre for Psychiatry, said: "These results suggest that the wider challenges and social circumstances facing certain ethnic minorities in specific deprived urban areas can explain significant variation in rates of diagnosed psychosis. To put it bluntly, 'place' should be seen as a risk factor in psychosis. That conclusion has significant implications for public health commissioners and services.
"Historical, political and social factors around place contribute to these health conditions. Place-based measures and interventions in early life are more likely to succeed than costly support or even punitive measures in later life."
He continued: "We believe that applying a syndemic approach in psychiatry is a significant advance. Our findings should be widely used in psychiatry and help shape preventive public health practice.
"Given the factors we have identified as risk factors for psychosis, the cuts we have seen in vital public health services such as drug and alcohol treatment and sexual health in recent years are both unfortunate and a false economy. A syndemic-based approach in research and practice can help design better prevention in healthcare—and inform the implementation of the NHS long term plan for England."
More information: Ethnic Disparities in Psychotic Experiences Explained by Area Level Syndemic Effects: Findings from the Second UK Men's Modern Lifestyles Survey. British Journal of Psychiatry (2019). DOI: 10.1192/bjp.2019.203