Staphylococcus aureus virulence tied to atopic dermatitis in infants

(HealthDay)—Skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus is associated with the risk for developing atopic dermatitis (AD), and infants who do not develop AD primarily exhibit acquisition of dysfunctional mutations in the S. aureus quorum-sensing system, according to a study published in the July 8 issue of Science Translational Medicine.
Yuumi Nakamura, M.D., Ph.D., from the Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan, and colleagues performed whole-genome sequencing of S. aureus strains isolated from the cheek skin of 268 Japanese infants at 1 to 6 months old to examine the role in AD development.
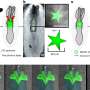
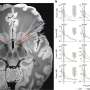
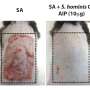
The researchers found that regardless of AD outcome, about 45 percent of infants were colonized with S. aureus at 1 month. At 6 months of age, skin colonization with S. aureus was associated with an increased risk for developing AD. Strains from 6-month-old infants who did not develop AD primarily exhibited acquisition of dysfunctional mutations in the S. aureus Agr quorum-sensing system. In mice, expression of a functional Agr system in S. aureus was necessary for epidermal colonization and AD-like inflammation induction.
"These studies show that retention of agr virulence is associated with increased S. aureus skin colonization and development of AD in Japanese infants," the authors write.
One author disclosed financial ties to Boehringer Ingelheim.
More information: Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2020 HealthDay. All rights reserved.