Around a third of infants with COVID-19 may have caught it from mother

Environmental exposure to SARS-CoV-2 was responsible for the majority of infections detected in newborn infants in an analysis of 176 reported cases. However, the findings, published in Nature Communications, suggest that 30% of the reported cases may have been acquired from the mother.
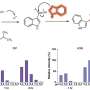
Daniele De Luca and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of published cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in neonates (within the first 30 days of life), as defined by at least one positive nasopharyngeal swab test and/or the detection of specific antibodies in the blood. In total, 176 cases were analysed, which had been reported up to 30 August 2020. The authors found that 70% of the cases resulted from environmental exposure. Thirty percent were likely the result of vertical transmission (transmission of the virus from mother to baby) and around 9% of the 176 cases were confirmed to be as a result of vertical transmission with infection acquired before or during childbirth.
55% of the infants (97) in the analysis went on to develop COVID-19 and the authors note that the clinical symptoms seem to be similar to those reported in older patients, including respiratory (52% of cases), fever (44%), and gastrointestinal (36%), and neurological (18%) symptoms.
When looking at infections that occurred at least 72 hours after birth, the authors found that infants in the sample who stayed in a crib next to their mother in hospital (roomed-in) appeared to have a higher incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infections. They argue that if rooming-in takes place, then appropriate hygiene measures and protective equipment should be made available to reduce the risk of transmission as a result of environmental exposure.
The authors also note that breastfeeding was not associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and they suggest that viral transmission through milk is rare, if at all. However, further studies are needed to confirm this.
More information: Roberto Raschetti et al. Synthesis and systematic review of reported neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections, Nature Communications (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18982-9