Meta-analysis quantifies lifestyle factors accounting for RA incidence

(HealthDay)—Nearly one-third of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) incidence is attributed to smoking, excess body mass index, and low alcohol consumption, according to a study published online Jan. 26 in BMJ Open.
Ding Ye, from the Zhejiang Chinese Medical University in Hangzhou, and colleagues quantified RA cases attributable to selected nongenetic risk factors in U.S. adults. The prevalence of exposure was obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. A meta-analysis was conducted to examine the correlations between modifiable risk factors and RA.
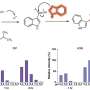
The researchers found that in the meta-analysis, the risks for RA were increased for former smokers and current smokers (relative risks, 1.22 and 1.47, respectively). The risk for RA was increased 1.27-fold for overweight and obese individuals. There was an 8 percent reduction in the risk for RA in association with each 50-g/week increment of alcohol consumption. The population-attributable fraction value of smoking was 14.0 percent. Excess body mass index accounted for 14.73 percent of RA incidence, while low alcohol intake accounted for 8.21 percent of RA risk. Overall, 32.69 percent of RA cases were attributed to smoking, overweight or obesity, and low alcohol consumption.
"In terms of actionable prevention for RA, currently there is likely enough evidence to recommend that to reduce risks for RA that individuals should stop smoking and maintain optimal body weight," the authors write.
More information: Abstract/Full Text
Copyright © 2020 HealthDay. All rights reserved.