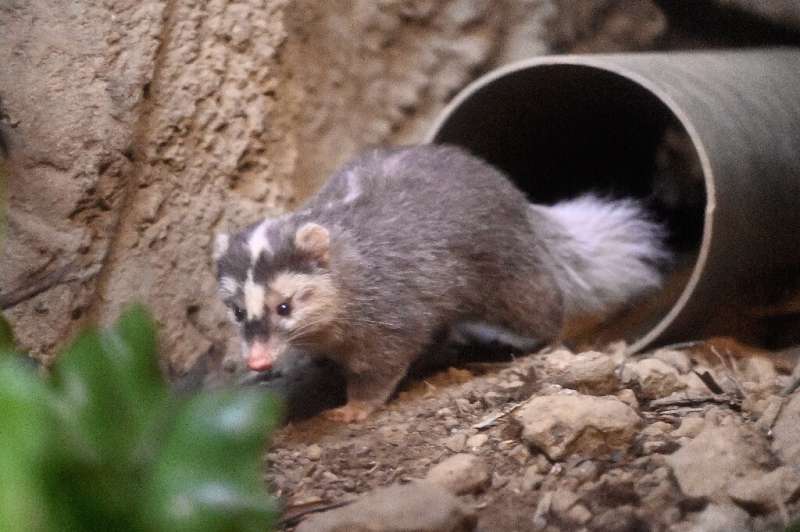
What is a ferret badger?

A number of animals have been suggested as the intermediary carrier of the coronavirus that has wracked the world for more than a year; most of them are familiar, but you might not have heard of the ferret badger. Here are some facts about this lesser-known creature.
What's in a name?
The ferret badger's name is actually fairly self-explanatory.
It's a member of the mustelidae, the family of mammals that includes weasels, badgers, ferrets, otters, martens, minks and wolverines.
Visually it looks very much like a cross between a ferret and a badger.
With an average length of 33 to 43 centimetres, its small size and thin shape is reminiscent of a ferret.
But they also have white facial markings and a stripe down their back, traits seen in many badger species.
The ferret badger looks quite similar to the palm civet cat which—while not a mustelidae—was identified as the intermediate host between bats and humans for the 2003 SARS outbreak.
Where would you find it?
The ferret badger has five identified sub-species, the Bornean, the Chinese, the Javan, the Burmese and the recently classified Vietnamese.
Chinese ferret badgers—melogale moschata—are the most widespread and can be found as far west as Assam in India, throughout southern China and as far east as Taiwan.
It has a diverse stomping ground and is found in tropical and subtropical forests as well as grasslands.
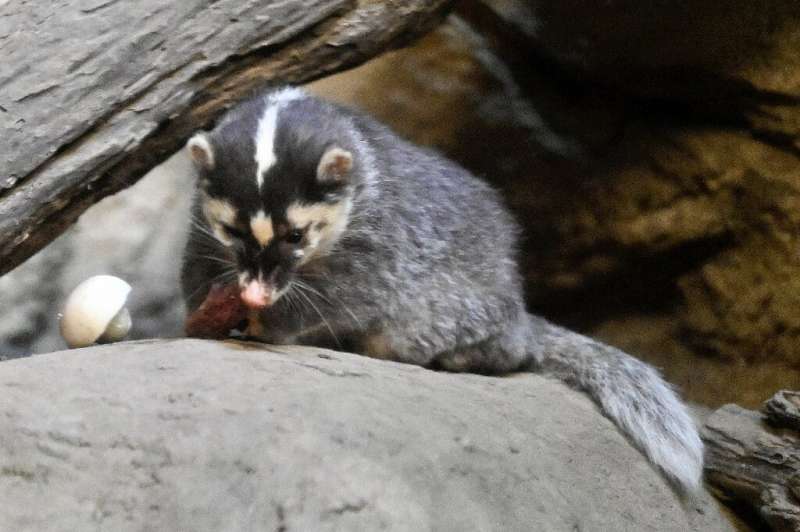

What's it like?
It is most active at dusk and during the night, eating an omnivorous diet of seeds, fruits and nuts as well as insects, earthworms and small amphibians.
It has sharp claws allowing it to climb—and sleep—in trees.
It also fiercely defends itself from threats, emitting a powerful smelling secretion from its anal glands when alarmed.
Is it endangered?
No, it is currently listed in the "least concern" category on the UN's Red List.
While it is sometimes hunted for its pelt, the ferret badger does not appear to be under any major population pressure.
Unlike many species, it may cope quite well with human encroachment onto its habitat.
A study of ferret badgers in the mid-1990s near a village in southeastern China found the animals often made use of firewood stacks and rock piles to rest and hunted for food in rice paddies, soybean, cotton, or grass fields.
Farmers usually liked the animals as they got rid of pests and did not tend to attack chickens or livestock.
© 2021 AFP