One in 20 COVID-19 cases report long-term symptoms
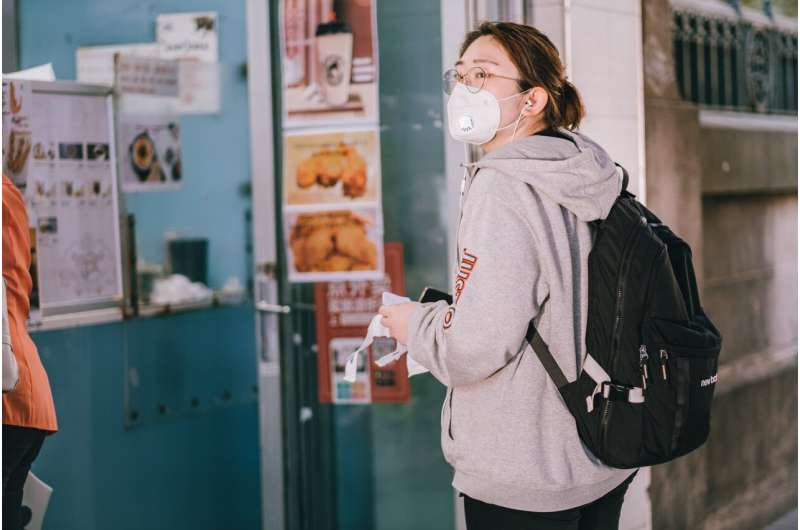

Five percent of people diagnosed with COVID-19 during NSW's 'first wave' were still experiencing symptoms three months later, according to the largest study of COVID-19 recovery time ever undertaken in Australia.
The study, a collaboration between UNSW Sydney and NSW Health and published in The Lancet Regional Health—Western Pacific journal today, also found younger people, men and those without co-morbidities generally recovered faster.
Using NSW's disease notification registry, linked health datasets, and telephone interviews with those infected, the comprehensive study systematically tracked 2904 people—almost everyone (94 percent) diagnosed with COVID-19 in NSW between January and May 2020.
The whole-of-population study is likely to provide more accurate estimates of the proportion of people who will experience long-term effects from COVID-19 than previous smaller studies. Many of these studies have been restricted to volunteers or those hospitalized with the virus, and some put the proportion of people experiencing long-term effects closer to 30 percent.
According to the study published today, three months after being diagnosed with COVID-19, 93.4 percent of people followed had recovered, most (80 percent) within 30 days, 1.8 percent had died and 4.8 percent were still experiencing symptoms. Of those who had still not recovered at the time of their last interview, the most commonly reported residual symptoms were cough and fatigue.
"We know a lot about acute clinical presentations where people end up in hospital, but much less about those who get less severe forms of the disease," said UNSW Associate Professor Dr. Bette Liu, lead author of the report.
"Our data demonstrates the substantial direct impact of COVID-19 on population health—and the need to consider not only hospitalisations and deaths, but also the longer-term health of those with less severe forms of the disease."
With more than 30,000 confirmed COVID-19 cases in Australia so far, "this study indicates that prolonged recovery from COVID-19 looks to be a significant problem for many Australians," said A/Prof. Liu.
"It is well known that COVID-19 severity increases with age and with the prevalence of other illnesses or underlying health conditions, so it's unsurprising that we found recovery was slower and less likely in these groups," A/Prof. Liu said.
There is a view among younger people that they would recover quickly from COVID-19, A/Prof. Liu said. "Although our study showed young people did recover more quickly, even among those aged under 30 we found that 2 percent were still experiencing some symptoms three months after diagnosis.
"This study demonstrates how important it is that we all protect ourselves from COVID-19 through following public health advice, including hand hygiene, physical distancing and testing, as well as getting vaccinated when it is your turn."
More information: Bette Liu et al, Whole of population-based cohort study of recovery time from COVID-19 in New South Wales Australia, The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100193