Looking at tumors through a new lens
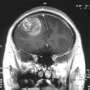
Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) is a promising treatment for melanoma and other cancer types, and has recently been shown to provide a modest survival benefit for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. To improve the treatment efficacy, researchers are looking for vulnerabilities in surgically removed glioblastoma tissues, but this has been difficult due to the vast differences within the tumors and between patients.
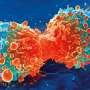
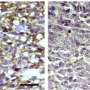
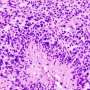
To address this challenge, researchers at Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and their collaborators developed a new way to study tumors. The method builds mathematical models using machine learning-based image analysis and multiplex spatial protein profiling of microscopic compartments in the tumor.
The team used the approach to analyze and compare tumor tissues collected from 13 patients with recurrent glioblastoma and 23 patients with high-risk melanoma, with both sets of patients treated with neoadjuvant ICB. Using melanoma to guide the interpretation of glioblastoma analyses, they identified the proteins that correlate with tumor-killing T cells, tumor growth, and immune cell-cell interactions.
"This work reveals similarities shared between glioblastoma and melanoma, immunosuppressive factors that are unique to the glioblastoma microenvironment, and potential co-targets for enhancing the efficacy of neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockade," said Dr. Yue Lu, co-lead author of the paper describing the research.
"This framework can be used to uncover pathophysiological and molecular features that determine the effectiveness of immunotherapies," added Dr. Alphonsus Ng, co-lead author of the paper.
The work was published today in Nature Communications, and is a collaborative project by ISB, UCLA and MD Anderson. Brain cancer represents one of the most challenging settings for achieving immunotherapy success. The fruitful collaboration between scientists and clinicians provides a tremendous opportunity for improving patient care and achieving an understanding of cancer immunotherapy at the deepest levels.
"We believe that the integrated biological, clinical and methodological insights derived from comparing two classes of tumors widely seen as at the opposite ends of the spectrum with respect to immunotherapy treatments should be of interest to broad scientific and clinical audiences," said ISB President Dr. Jim Heath, corresponding author of the paper.
More information: Yue Lu et al, Resolution of tissue signatures of therapy response in patients with recurrent GBM treated with neoadjuvant anti-PD1, Nature Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24293-4