WHO decision challenges West to recognize Chinese vaccines
The World Health Organization said Thursday that any COVID-19 vaccines it has authorized for emergency use should be recognized by countries as they open up their borders to inoculated travelers.
The move could challenge Western countries to broaden their acceptance of two apparently less effective Chinese vaccines, which the U.N. health agency has licensed but most European and North American countries have not.
In addition to vaccines by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna Inc., AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, the WHO has also given the green light to the two Chinese jabs, made by Sinovac and Sinopharm.
In its aim to restore travel across Europe, the European Union said in May that it would only recognize people as vaccinated if they had received shots licensed by the European Medicines Agency—although it's up to individual countries if they wish to let in travelers who have received other vaccines, including Russia's Sputnik V.
The EU drug regulator is currently considering licensing China's Sinovac vaccine, but there is no timeline on a decision. It also does not recognize versions of the AstraZeneca vaccine that were made in India, effectively barring travel for people in developing countries who received doses via the U.N.-backed initiative known as COVAX.

"Any measure that only allows people protected by a subset of WHO-approved vaccines to benefit from the reopening of travel ... would effectively create a two-tier system, further widening the global vaccine divide and exacerbating the inequities we have already seen in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines," a WHO statement said Thursday. "It would negatively impact the growth of economies that are already suffering the most."
The WHO said such moves undermine "confidence in life-saving vaccines that have already been shown to be safe and effective." In its reviews of the two Chinese vaccines, the U.N. health agency said both were found to significantly reduce the risk of hospitalizations and deaths.
The two Chinese shots are "inactivated" vaccines, made with killed coronavirus, whereas the Western-made shots are made with newer technologies that instead target the "spike" protein that coats the surface of the coronavirus.
-
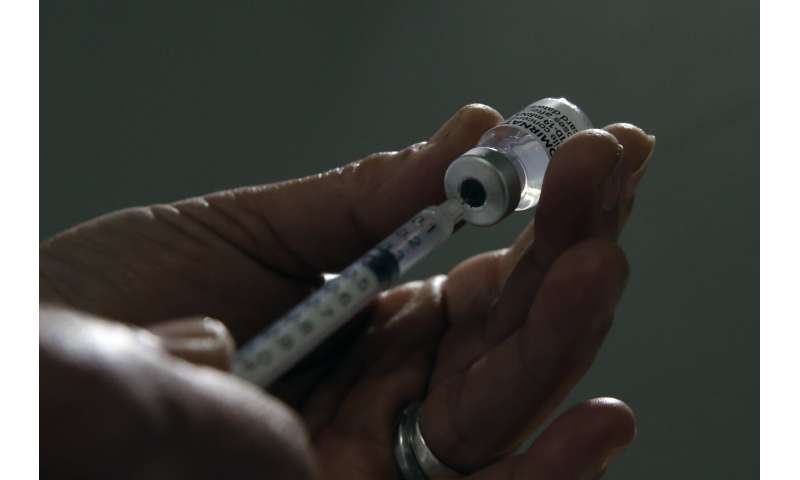
In this file photo dated Sunday, April 4, 2021, a member of the medical staff prepares a dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, at a vaccination site in Sarcelles, outside Paris. The World Health Organization said that any COVID-19 vaccines it has authorized for emergency use should be recognized by countries as they open up their borders, in a move that could challenge Western countries to broaden their acceptance of two Chinese vaccines which the U.N. health agency has licensed, but most European and North American countries have not. Credit: AP Photo/Christophe Ena, File -
In this file photo dated Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, three vials of the Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine are pictured in a new coronavirus vaccination center at the 'Velodrom' (velodrome-stadium) in Berlin, Germany. The World Health Organization said that any COVID-19 vaccines it has authorized for emergency use should be recognized by countries as they open up their borders, in a move that could challenge Western countries to broaden their acceptance of two Chinese vaccines which the U.N. health agency has licensed, but most European and North American countries have not. Credit: AP Photo/Michael Sohn, File
Although Western countries have largely relied on vaccines made in the U.S. and Europe, such as Pfizer-BioNTech and AstraZeneca, many developing countries have used the Chinese-made shots.
Earlier this year, the head of China's Center for Disease Control and Prevention acknowledged the effectiveness of its home-grown shots was low. Numerous countries that have used millions of doses of the two Chinese shots, including the Seychelles and Bahrain, have seen COVID-19 surges even with relatively high levels of immunization.
© 2021 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.