Developing treatment for vision loss through transplant of photoreceptor precursors
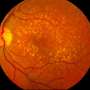
Inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) are a group of genetically and clinically homogeneous illnesses characterized by progressive retinal damage leading to vision loss. The global incidence of IRDs is approximately 1 in 2000 persons. These disorders are amongst some of the leading causes of blindness worldwide.
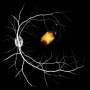
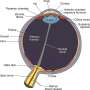
While the introduction of gene therapy has been a significant development, its effectiveness has been blunted by the sheer extent of genetic heterogeneity, with more than 260 genes implicated in IRDs. This limits the widespread application of gene therapy for all IRDs. Additionally, gene therapy has limited efficacy in clinical cases of advanced retinal degeneration in which significant photoreceptor cell death has already occurred. Photoreceptor cells are found in the retina and respond to light, converting it into electrical signals that activate physiological chain reactions. These signals are sent through the optic nerve to the brain for processing.
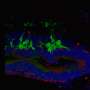
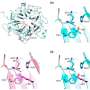
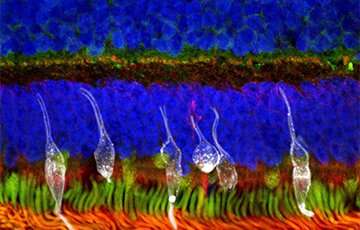
With the advent of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) and embryonic stem cell (ESC) technology, regenerative stem cell therapy has the potential to be an alternative treatment for end-stage retinal degeneration, independent of the underlying genetic defect. Retinal regenerative therapies therefore hold great promise for the treatment of IRDs. Studies in animal models of IRDs have suggested visual improvement following retinal photoreceptor precursors transplantation, though there is limited evidence on the ability of these transplants to rescue retinal damage in higher mammals.
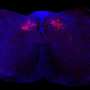
A recently published study in the journal Stem Cell Research and Therapy led by Assistant Professor Su Xinyi from the Department of Ophthalmology at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine examines the therapeutic potential of photoreceptor precursors derived from clinically compliant iPSCs. The study demonstrated the safety and therapeutic potential of clinically compliant iPSC-derived photoreceptor precursors as a cell replacement source for future clinical trials. These include performing a first-in-man clinical trial for photoerecptor precursor transplant in Singapore, in collaboration with RxCELL, a biotechnology company focused on therapeutic applications iPSCs.
More information: Lingam, S. et al. cGMP-grade human iPSC-derived retinal photoreceptor precursor cells rescue cone photoreceptor damage in non-human primates. Stem Cell Res Ther (2021). doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02539-8 , stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/ … 6/s13287-021-02539-8