Machine learning models predict hepatocellular carcinoma treatment response
According to research publsihed in the American Journal of Roentgenology, machine learning models applied to presently underutilized imaging features could help construct more reliable criteria for organ allocation and liver transplant eligibility.
"The findings suggest that machine learning-based models can predict recurrence before therapy allocation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) initially eligible for liver transplant," wrote corresponding author Julius Chapiro from the department of radiology and biomedical imaging at Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, CT.
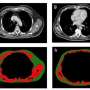
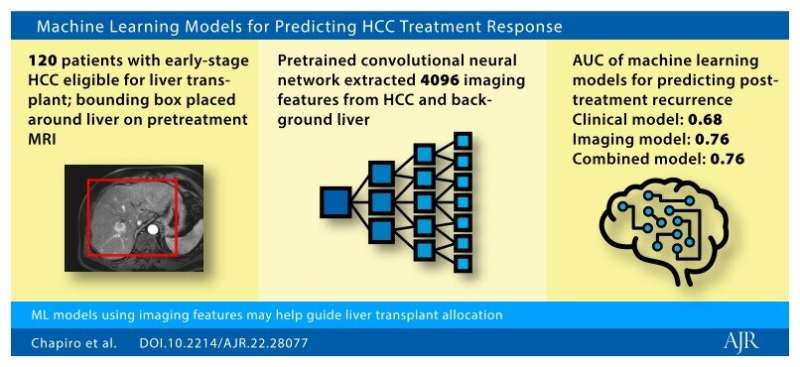
Chapiro and colleagues' proof-of-concept study included 120 patients (88 men, 32 women; median age, 60 years) diagnosed with early-stage HCC between June 2005 and March 2018, who were initially eligible for liver transplant and underwent treatment by transplant, resection, or thermal ablation. Patients underwent pretreatment MRI and posttreatment imaging surveillance, and imaging features were extracted from postcontrast phases of pretreatment MRI examinations using a pretrained convolutional neural network (VGG-16). Pretreatment clinical characteristics (including laboratory data) and extracted imaging features were integrated to develop three ML models—clinical, imaging, combined—for recurrence prediction within 1–6 years posttreatment.
Ultimately, all three models predicted posttreatment recurrence for early-stage HCC from pretreatment clinical (AUC 0.60–0.78, across all six time frames), MRI (AUC 0.71–0.85), and both data combined (AUC 0.62–0.86). Using imaging data as the sole model input yielded higher predictive performance than clinical data alone; however, combining both data types did not significantly improve performance over use of imaging data alone.
More information: Simon Iseke et al, Machine-Learning Models for Prediction of Posttreatment Recurrence in Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Pretreatment Clinical and MRI Features: A Proof-of-Concept Study, American Journal of Roentgenology (2022). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.22.28077