This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Rhinoviruses, enteroviruses persisted during pandemic among pediatric patients
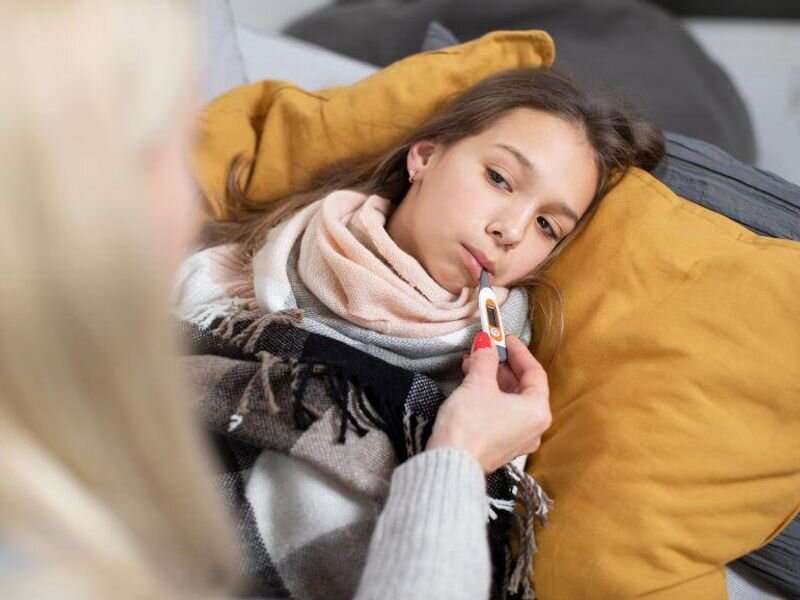

Rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses persisted during the pandemic for children and adolescents, according to a study published online Feb. 7 in JAMA Network Open.
Danielle A. Rankin, Ph.D., M.P.H., from the Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues quantified and characterized rhinovirus and/or enterovirus detection before and during the COVID-19 pandemic among 38,198 children and adolescents seeking medical care for acute respiratory illness at emergency departments or hospitals.
The researchers found that rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses were detected in 29.4 and 30.9 percent of all patients who were enrolled and tested in the prepandemic and pandemic periods, respectively, and in 42.2 and 73.0 percent of those with test positivity for any virus in the prepandemic and pandemic periods, respectively. In both periods and in all age groups, rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses were the most frequently detected viruses in the emergency department and inpatient settings.
Rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses were detectable at similar or lower odds from April to September 2020 compared with the prepandemic eras, with adjusted odds ratios ranging from 0.08 to 0.76 in the emergency department and 0.04 to 0.71 in the inpatient setting. Rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses soon returned to prepandemic levels and were detected at similar or higher odds than in prepandemic months in both settings from October 2020 to February 2021, with adjusted odds ratios ranging from 1.47 to 3.01 and 1.36 to 2.44, respectively, and in all age groups.
"Persistence of rhinoviruses and/or enteroviruses, and to some degree adenoviruses, when other respiratory viruses were substantially curtailed suggests that nonenveloped viruses were less affected by the various combinations of nonpharmaceutical interventions implemented," the authors write.
Several authors disclosed financial ties to the biopharmaceutical industry.
More information: Danielle A. Rankin et al, Circulation of Rhinoviruses and/or Enteroviruses in Pediatric Patients With Acute Respiratory Illness Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the US, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.54909
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.