This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Accounting for diversity in robot design, testbeds, and safety standardization

Robots in medical care and rehabilitation are becoming increasingly prevalent. They promise to meet patients' needs by personalizing physical and social interactions with users. However, tailoring robots to users is about more than just making the robot adjustable or personalized to the users' tastes. It is also about ensuring design justice (i.e., a design theory that rethinks design processes, places marginalized groups at the center of the design process, and exploits collaborative, creative practices to overcome exclusion challenges) and understanding how inclusive robot design is to interact with the user in a natural, non-discriminatory way.
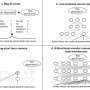
Following an extensive literature review and two weeks of experimentation within a robotic testbed developed under the H2020 EUROBENCH project for lower-limb exoskeletons in Los Madroños Hospital in Madrid (Spain), Eduard Fosch-Villaronga from eLaw and Hadassah Drukarch realized that many diversity considerations, including gender, health condition, age, and body complexity, are safety-critical and their disregard in robot designs, robot testing zones, and standards can cause harm to users. They published their observations in the International Journal of Social Robotics.
While research often calls out developers and designers for failing to account for diversity, in this article, they focused on how and to what extent existing lower limb exoskeletons, robot testbeds, regulations and standards account for users coming in different sizes, shapes, and medical conditions. More specifically, they focused on ISO 13482:2014 on Personal Care Robots, the leading standard setting out safety requirements for personal care robots (i.e., service robots increasing the standard of living of humans, excluding medical or industrial applications.
Departing from their experiments and observations conducted under the H2020 EUROBENCH Financial Support to Third Parties (FSTP) PROPELLING project, the researchers argue that the standard insufficiently accounts for differences between users, potentially compromising the safety of subjects whose features remain ignored.
More information: Eduard Fosch-Villaronga et al, Accounting for Diversity in Robot Design, Testbeds, and Safety Standardization, International Journal of Social Robotics (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s12369-023-00974-6