This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Nearly all quality care measures, visits decreased substantially at federally qualified health centers during COVID
Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) provide comprehensive preventive care, chronic disease management, and mental health and substance use services to more than 30 million low-income and majority non-White patients who would otherwise likely lack access to these critical services.
While FQHCs have played a pivotal role in ensuring equitable access to COVID-19 treatments and vaccines, the populations served by FQHCs have also been disproportionately affected by COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths, making continuity of quality care even more essential during the pandemic.
But now, a new study led by a School of Public Health researcher has found that nearly all FQHC quality-of-care performance measures, as well as overall visit volumes, plummeted during the first year of the pandemic, and these decreases persisted into 2021.
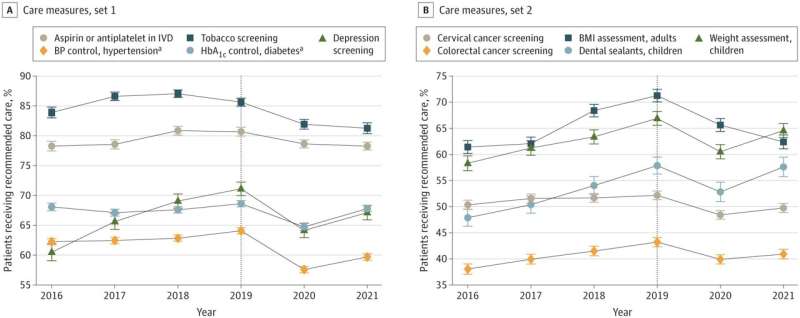
Published in the journal JAMA Health Forum, the study found that 10 of 12 FQHC quality-of-care performance measures declined substantially during this period, including measures for cervical and colorectal cancer screenings, weight assessment and counseling, depression screening, tobacco use screening and cessation, and hypertension and glucose control, among others.
Similarly, the majority of 41 different FQHC visit types declined during these first two years of COVID, including visits for immunizations, oral examinations, and supervision of infant or child health.
Notably, while most FQHC visit types decreased in 2020 and 2021, patient visits for substance use disorder, depression, anxiety, and sexually transmitted infections increased after the pandemic began in 2020, and continued to increase in 2021.
The study is the first nationally comprehensive assessment of the performance of FQHCs during the first two years of COVID.
"Our findings suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted years of FQHC progress in improving quality measures and expanding patient service volumes. Moving forward, FQHCs will need sustained federal funding to expand FQHC service capacity, staffing, and patient outreach in order to compensate for missed care during COVID-19," says study corresponding author Megan Cole, associate professor of health law, policy & management.
"At the same time, FQHCs have played an important role in meeting increased need for behavioral health services likely exacerbated by the pandemic, and continued investments into FQHC behavioral health workforce will be needed to ensure these growing needs are met."
For the study, Cole and colleagues from the University of Washington School of Medicine and the University of South Carolina Arnold School of Public Health utilized national healthcare data from the Health Resources and Services Administration to examine quality-of-care measures and visit volumes among nearly 27 million patients at FQHCs before (2016 to 2019) and during (2020 to 2021) the first two years of the pandemic.
By 2021, only one of the 10 quality measures that had declined in 2020 returned to 2019 levels: dental sealants for children. Tobacco screenings and BMI assessments continued to decline even further in 2021. The majority of the 28 visit volume measures that declined in 2020 remained below pre-pandemic rates in 2021.
In addition to continued funding, the researchers also emphasize that quality reporting and value-based care models must also adapt to the shorter- and longer-term impacts of the pandemic on quality measures.
"This is particularly important for entities such as accountable care organizations and managed care plans whose finances and operations are determined by quality performance measures," says Cole.
The journal also published an accompanying editorial, titled "Sustaining Key Services in Federally Qualified Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic," by Ayanian and Miguel Marino.
More information: Megan B. Cole et al, Changes in Performance Measures and Service Volume at US Federally Qualified Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic, JAMA Health Forum (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0351
John Z. Ayanian et al, Sustaining Key Services in Federally Qualified Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic, JAMA Health Forum (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0347