This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Review highlights effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on multiple organ systems
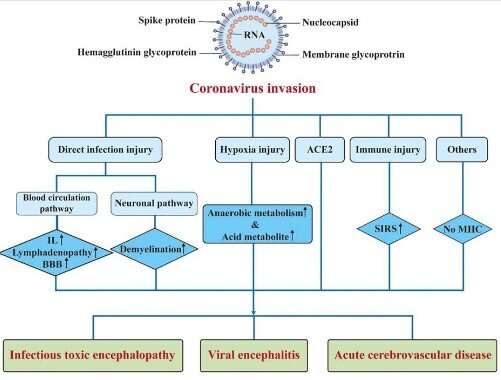
A new review article published in the Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences offers valuable insights into the multi-organ system damage caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The article, titled "SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Multi-Organ System Damage: A Review," is authored by Ali A. Rabaan of the Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory, Johns Hopkins Aramco Healthcare, Saudi Arabia, and Ebtesam Al-Suhaimi of the Biology Department, College of Science and Institute for Research and Medical Consultations (IRMC), Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Saudi Arabia.
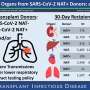
The authors provide a comprehensive overview of the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on multiple organ systems, including respiratory, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, nervous, endocrine, reproductive, immune, and parts of the integumentary system. They emphasize that although the respiratory system is most affected, the virus can spread hematogenously and infect various organs, causing severe and long-term complications even after the disease has ended.
"The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed the complex and multifaceted nature of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Our review highlights the need for a more in-depth understanding of the wide-ranging impact of the virus on the human body," said Ali A. Rabaan.
The authors also point out the importance of redesigning diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to address organ-specific damage caused by the virus. They note the increased risk of COVID-19 complications in older adults and those with preexisting conditions.
Ebtesam Al-Suhaimi stated, "By comprehensively examining the latest research on the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on multiple organs and systems, our study aims to contribute to improved disease surveillance, transmission prevention, and management of multi-organ-system complications."
The review also emphasizes the significance of understanding the range of atypical COVID-19 symptoms to improve disease surveillance, limit transmission, and avoid additional multi-organ-system problems.
In conclusion, the review article provides critical knowledge for medical professionals, researchers, and public health officials worldwide, as they continue to battle COVID-19 and its far-reaching consequences.
More information: Ali A. Rabaan et al, SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and multi-organ system damage: a review, Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7762