This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Rituximab not noninferior to ocrelizumab for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis

For patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS), rituximab is not noninferior to ocrelizumab, according to a study published online June 12 in JAMA Neurology.
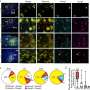
Izanne Roos, M.B.Ch.B., Ph.D., from Royal Melbourne Hospital in Australia, and colleagues examined whether the effectiveness of rituximab is noninferior to ocrelizumab in relapsing-remitting MS in an observational cohort study. Participants had a history of relapsing-remitting MS treated with ocrelizumab or rituximab, a minimum follow-up of six months, and sufficient data to calculate the propensity score. The analysis included 710 patients treated with ocrelizumab and 186 treated with rituximab.
The researchers found that the annualized rate of relapses ratio was higher in patients treated with rituximab versus ocrelizumab (rate ratio, 1.8) over a pairwise censored mean follow-up of 1.4 years. Compared with patients treated with ocrelizumab, those treated with rituximab had a higher cumulative hazard of relapses (hazard ratio, 2.1). There was no difference between the groups in the risk for disability accumulation. In sensitivity analyses, results were confirmed.
"Treatment selection for the individual patient, however, remains a complex and highly personalized decision, which considers additional factors such as availability and affordability of therapy and adverse effects," the authors write. "Nevertheless, lack of a clinically relevant difference in the effectiveness between these two therapies should not be assumed."
Several authors disclosed ties to the pharmaceutical industry; several pharmaceutical companies provided funding for the study.
More information: Izanne Roos et al, Rituximab vs Ocrelizumab in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis, JAMA Neurology (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1625
Lauren Oommen et al, New Approaches to Challenge Old Assumptions—B-Cell Depletion in Multiple Sclerosis, JAMA Neurology (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1079
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.