This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Yearly scanning not required for common brain tumor detected in 1 in 10 people, study shows
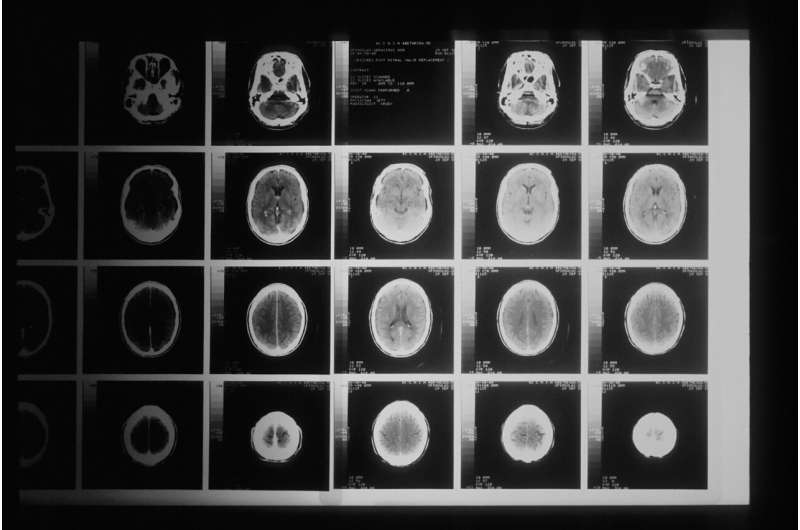
People with a common type of benign brain tumor detected in around one in 10 don't require annual scans, a new national UK study has found.
The largest study of its kind has been published in the European Journal of Endocrinology and looks at clinical data on a type of tumor growth in the pituitary gland in the brain. The common growth, called a non-functioning pituitary microadenoma (NFPA), is less than 1cm across, is predicted to affect around 10% of the population and usually doesn't cause any symptoms.
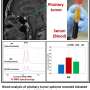
In the UK-wide study, 419 people were monitored for NFPAs across 23 specialist sites. A team of endocrinologists led by Dr. Niki Karavitaki from the University of Birmingham found that NFPAs were almost twice as likely to shrink or disappear by themselves (14% likelihood) as to grow (7.8% likelihood) within the first three years of monitoring. Among those tumors that grew, average (median) growth of tumors was 2mm, and eight participants' tumors were surgically removed and only one of them had any visual impairment.
Dr. Niki Karavitaki, Clinical Associate Professor in Endocrinology in the Institute of Metabolism and Systems Research at the University of Birmingham and last author of the paper said,
"These data are the best picture that we have in the UK of how these common tumors progress over a period of three to five years. The results show that most people, who are often diagnosed with these tumors as part of an unrelated scan, don't need annual check on these tumors with the majority of adenomas either remaining the same size or shrinking."
First author of the paper was Dr. Ross Hamblin, MD student at the University of Birmingham and the findings have led the research group, called the UK NFPA Consortium to suggest that clinical guidelines should be changed due to the low risk of these common tumors developing into a health risk for most people. The Consortium suggest that a single scan three years after initial detection would be a safe and more cost-effective way to manage NFPAs.
Dr. Karavitaki said, "At the moment, people are often being re-scanned on an annual basis during the first years from the initial detection of the tumor without a really clear clinical rationale, and our results show that for those with microadenomas those scans are unnecessary which can lead to space being freed up for other conditions."
"Our recent survey of UK clinicians has found a significant variation in frequency of scans and we believe that on this research should be a strong steer that a more cost-effective approach is still safe for patients due to the very low risks involved."
More information: Ross Hamblin et al, Natural history of non-functioning pituitary microadenomas—results from the UK NFPA consortium, European Journal of Endocrinology (2023). DOI: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad070