This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Restrictions on postpartum public insurance endanger health of immigrant moms, study reveals
When immigrants gave birth in a U.S. state that limits postpartum public insurance eligibility based on their immigration status, they are less likely to receive medical care following childbirth, a study published July 18 in JAMA shows.
"Compared to states without insurance restrictions, immigrants in states with public insurance restrictions for postpartum immigrants are less likely to receive postpartum care," write Maria W. Steenland of Brown University, Laura R. Wherry of New York University, Rachel Fabi at SUNY Upstate Medical University, and their colleagues. Hence, "Restricting public insurance coverage may be an important policy-driven barrier to receipt of recommended pregnancy care and improved maternal health among immigrants."
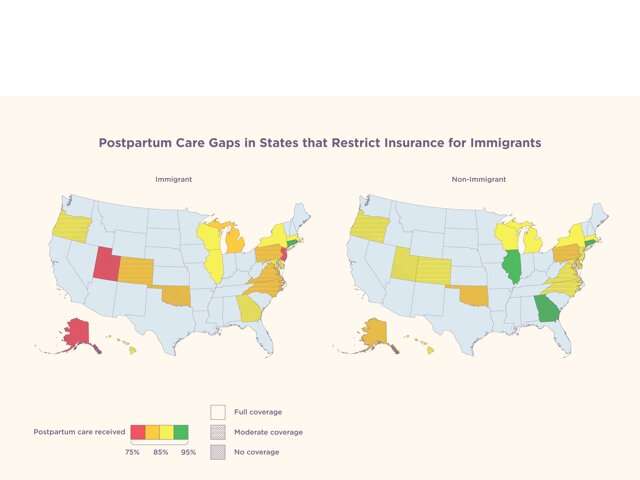
The new study looks at data on 19 states and New York City and a total of 72,981 low-income women who gave birth between 2012 and 2019. Of the states examined by the researchers, 10 offer coverage for recently documented but not undocumented immigrants, and four offer no coverage to either immigrant group.
The 10 states with coverage for recently documented but not undocumented immigrants that were included in the study were Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Virginia. The four states with no coverage for either immigrant group were Alaska, Georgia, Oklahoma, and Utah.
In the opinion expressed by major professional associations for physicians and medical students, postpartum care is necessary to provide diagnosis and treatment of postpartum health concerns and ensure the health and well-being of postpartum individuals. An additional six states the researchers examined—Illinois, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New York, Oregon, and Rhode Island—offered coverage for postpartum care for both recently-documented and undocumented immigrants.
The pool of postpartum individuals covered by the research data for the study encompassed 20,971 immigrants (29%) and 52,010 non-immigrants (71%). The number of immigrants receiving postpartum care was found to be 11.3 percentage points lower in states with no coverage for recently documented and undocumented immigrants and 7 percentage points lower in states with coverage only for recently documented immigrants, when compared to immigrants in states that covered postpartum care for both of these groups.
As the study notes, deaths of women in connection with pregnancy or childbirth are higher in the U.S. than in any other high-income nation. Reflecting the importance that professional medical organizations place on postpartum services, 65% of pregnancy-related deaths occur at least one day after childbirth in the U.S., and 30% occur between six weeks and one year after childbirth. During a postpartum visit, women can be diagnosed and treated for common conditions that cause maternal mortality, such as postpartum depression and postpartum hypertension.
Titled "State public insurance coverage policies and postpartum care among immigrants," the study comes after 33 states and the District of Columbia have amended, at different times since 2021, their Medicaid policies to cover postpartum medical care through 12 months after delivery, up from the prior limit of 60 days for postpartum care. However, since these policy changes extending the availability of health services began to emerge, only a handful of states have opted to include undocumented immigrants under it.
Among all low-income women of reproductive age in the U.S., 48% of noncitizens are medically uninsured, compared to 16% of U.S.-born women.
The study responds to a paucity of available data on postpartum care receipt among low-income immigrants and on the role of state coverage policies in the health of immigrant women and children. As representative data are scarce at both the state and national levels, the authors created an original dataset, using representative pregnancy surveillance data at the state level and state birth certificates indicating maternal country of origin. This linked data enabled the researchers to document postpartum care receipt by low-income immigrants, which had not previously been studied beyond the local level.
In addition, a detailed state policy review conducted as part of the study determined the extent of public insurance for postpartum immigrants, offering the first available evidence on the relationship between state public insurance for postpartum immigrants and postpartum care receipt among low-income immigrants.
"While public health insurance plays a huge role in financing pregnancy related postpartum care of low-income pregnant people in the U.S., public insurance coverage options are limited for undocumented and recent immigrants," according to the study.
"In half of U.S. states, documented immigrants must wait five years after establishing legal residence (often referred to as a waiting period) to obtain pregnancy Medicaid. Meanwhile, undocumented immigrants are ineligible for coverage in the majority of states."
More information: Maria W. Steenland et al, State Public Insurance Coverage Policies and Postpartum Care Among Immigrants, JAMA (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.10249