This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study finds limitations to CPR directions given by AI voice assistants, recommends use of emergency services
When Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is administered out of the hospital by lay persons, it is associated with a two- to four-fold increase in survival. Bystanders may obtain CPR instructions from emergency dispatchers, but these services are not universally available and may not always be utilized. In these emergency situations, artificial intelligence voice assistants may offer easy access to crucial CPR instructions.
Researchers at Mass General Brigham, New York's Albert Einstein College of Medicine, and Boston Children's Hospital investigated the quality of CPR directions provided by AI voice assistants. They found that the directions provided by voice assistants lacked relevance and came with inconsistencies. These findings have been published in JAMA Network Open.
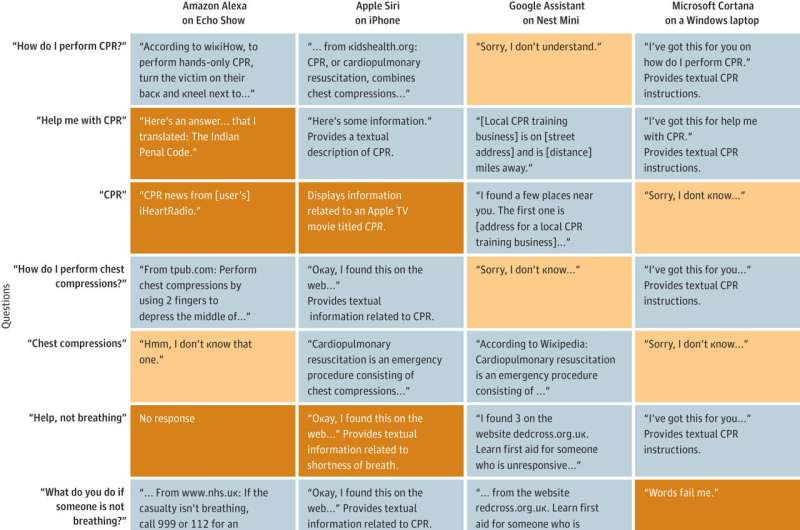
Researchers posed eight verbal questions to four voice assistants, including Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri, Google Assistant's Nest Mini, and Microsoft's Cortana. They also typed the same queries into ChatGPT. All responses were evaluated by two board certified emergency medicine physicians.
Nearly half of the responses from the voice assistants were unrelated to CPR, such as providing information related to a movie called CPR or a link to Colorado Public Radio News, and only 28% suggested calling emergency services. Only 34% of responses provided CPR instruction and 12% provided verbal instructions. ChatGPT provided the most relevant information for all queries among the platforms tested.
Based on these findings, the authors concluded that use of existing AI voice assistant tools may delay care and may not provide appropriate information. Limitations to this study included the asking of a small number of questions and not characterizing if the voice assistants' responses changed over time.
"Our findings suggest that bystanders should call emergency services rather than relying on a voice assistant," said senior author Adam Landman, MD, MS, MIS, MHS, chief information officer and senior vice president of digital at Mass General Brigham and an attending emergency physician. "Voice assistants have potential to help provide CPR instructions, but need to have more standardized, evidence-based guidance built into their core functionalities."
More information: Quality of Layperson CPR Instructions From Artificial Intelligence Voice Assistants, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31205