This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Racial discrimination linked to increased inflammation among Black women with systemic lupus erythematosus, study finds
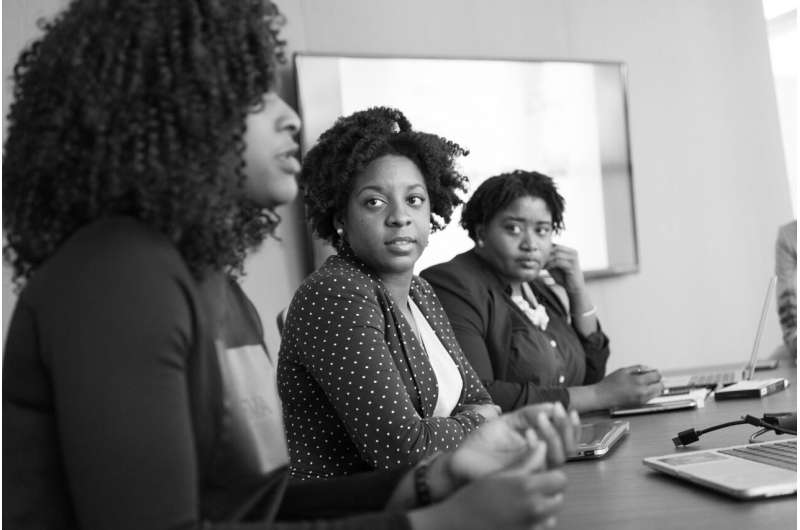

New research from the Black Women's Experiences Living with Lupus (BeWELL) Study has revealed that racial discrimination is a distinct health threat that heightens the risk of disease among Black Americans. The research, focused on Black women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an inflammatory autoimmune disease, sheds light on the detrimental effects of psychosocial stress on health and the role of inflammatory mechanisms. The study was published in the journal Brain, Behavior and Immunity.
Over a two-year period, the BeWELL Study examined incident experiences of racial discrimination and changes in the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein (CRP)—a protein made by the liver that increases when there's inflammation in the body—among 380 participants from metropolitan Atlanta, Georgia. The study, which enrolled participants from April 2015 to May 2017, utilized the Experiences of Discrimination measure to assess racial discrimination bi-annually through self-report. CRP levels were measured annually.
The findings of the study revealed a significant association between incident racial discrimination and elevated CRP levels throughout the two-year study period. The increase in CRP levels was substantial, with each domain of racial discrimination experienced resulting in a nearly 4% rise.
"This study contributes to the growing body of evidence on the biological consequences of racial discrimination," said Dr. Tamika Webb-Detiege, a rheumatologist and deputy head of admissions and enrollment academic for the University of Queensland /Ochsner Clinical School. "Understanding how racial discrimination compromises health and inflammatory pathways is crucial in our pursuit of more equitable and just outcomes for our communities."
The study's findings provide valuable insights into the racial inequities observed in outcomes for Black women with diseases driven by inflammatory pathways. By highlighting the role of racial discrimination in exacerbating health disparities, this research underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions and policies to address systemic racism and promote health equity.
As racial discrimination continues to pose a significant health threat to Black Americans, it is imperative that health care providers, policymakers, and communities work together to dismantle systemic barriers and create a more inclusive and just society. This study serves as a call to action, urging stakeholders to prioritize the elimination of racial discrimination and its detrimental effects on health.
More information: Connor D. Martz et al, Incident racial discrimination predicts elevated C-Reactive protein in the Black Women's experiences Living with Lupus (BeWELL) study, Brain, Behavior, and Immunity (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.06.004