This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Small study suggests long COVID may affect more people than previously thought

Millions of Americans were exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, early in the pandemic but could not get diagnosed due to testing limitations. Many of those people developed a post-viral syndrome with symptoms similar to those of long COVID. In a new study of a small group of those people, their immune response shows that 41% had evidence of SARS-CoV-2 exposure. The study is published in Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation.
"Since most long COVID clinics are only accepting patients with a positive test result, these people experiencing identical symptoms are left without specialized care and excluded from research studies on long COVID," said study author Igor J. Koralnik, MD, of Northwestern Medicine Comprehensive COVID-19 Center in Chicago and a Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Our data suggest that millions of Americans with post-viral syndrome may have been exposed to SARS-CoV-2 at the beginning of the pandemic, and they deserve the same access to care and inclusion in research studies as people with a confirmed COVID diagnosis."
The small study involved 29 people with post-viral syndrome including neurologic symptoms such as problems with memory and thinking skills, headache and fatigue but who did not have a positive COVID test result. They were matched with 32 people of similar age with long COVID and positive test results. Both groups were also compared to 18 people with none of those symptoms and no known exposure to COVID or positive test result.
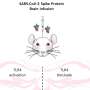
Researchers tested the participants for antibodies to two types of proteins that show an immune response that indicate a prior COVID infection—nucleocapsid protein and spike protein. Of the 29 people with post-viral syndrome, 12 people, or 41%, had immune responses consistent with prior exposure to COVID and similar to the long COVID group. Three-quarters had responses against the nucleocapsid protein and one-half had responses against the spike protein.
That group also had similar symptoms to the long COVID group and similar results on tests of thinking skills.
"Unlike our clinic, about 70% of post-COVID clinics in the U.S. do not accept people with long COVID symptoms who do not have a positive test result for COVID," Koralnik said. "Our data suggest that at least four million people with post-viral syndrome similar to long COVID may indeed have detectable immune responses to support a COVID diagnosis. More research is needed to confirm our findings."
A limitation of the study is the small number of people with post-viral syndrome. Also, some of the participants may have tested positive for COVID-19 immune responses if their blood samples were collected closer to when their symptoms began.
More information: Igor J. Koralnik et al, Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation (2023).