This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
COVID-19: Report explores link between state's geographic regions and impact of the pandemic
The latest report from University of Michigan public health researchers studying how COVID-19 affected Michiganders found that the severity of illness or negative impact of the pandemic is strongly linked to where one lives.
The report, Geographic Differences in Access to Care, Recovery, and the Social Impact of COVID-19 in Michigan, is the eighth in a series of reports compiled from the Michigan COVID-19 Recovery Surveillance Study, or MI CReSS.
The reports break down experiences and the effects of the virus and the pandemic on Michigan residents' health, work, finances, personal life, mental health and more.
A U-M public health team led by Nancy Fleischer, associate professor of epidemiology in the School of Public Health, culls data from surveys of more than 5,500 Michigan residents and produces reports for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
The goal of the partnership is to gather and share information that public health leaders may use to better support and protect residents when future public health threats and emergencies arise.
"This latest report highlights important differences across regions in Michigan in terms of access to care, the severity of disease and the social impact of illness and the pandemic," Fleischer said. "Some of the differences that we see across regions may be due to underlying population vulnerabilities.
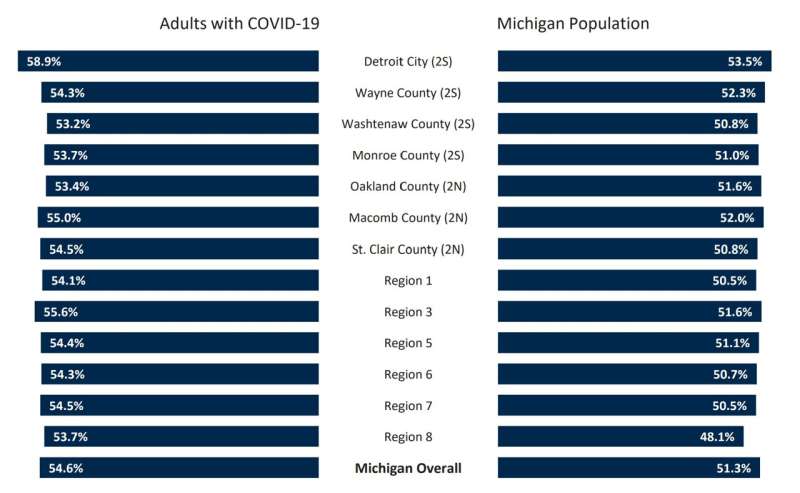
"For example, Detroit had the highest proportion of adults with severe disease, and also experienced many of the social impacts, including job loss, reduced work hours and difficulty paying bills."
U-M School of Public Health researcher Akash Patel evaluated the data to produce the latest report. The findings are based on responses from more than 5,500 Michiganders who had COVID-19 prior to June 1, 2022. Their responses are compared by where they live. Some noteworthy data points:
- Detroit had the highest proportion of adults with severe disease based on responses about symptom severity and hospitalization, while the southwest region of the state had the highest proportion of adults with long COVID—persistent symptoms 90+ days after COVID-19 onset. Washtenaw County had the lowest proportion reporting severe disease or long COVID.
- Detroit had the highest proportion of residents without private health insurance, and the greatest proportion to delay COVID-19 care due to cost or other barriers.
- In Detroit and Macomb County, nearly 1 in 4 employed adults who worked in person lacked regular access to personal protective equipment at work.
- More than 90% of respondents in Monroe and St. Clair counties said their physical presence was required at work, while nearly 40% of respondents in Oakland County reported not taking sick leave while ill.
"These findings highlight the importance of consistent social, economic and medical support for communities to avoid the most severe consequences of public health emergencies," Fleischer said. "While some challenges from COVID-19 illness and the pandemic were universal, others were more challenging for some Michiganders based on resources that were already in place prior to the pandemic."
The current report asked questions such as:
- Who lost jobs and wages? Who took sick leave or paid sick leave? Who lacked personal protective equipment at work? Who was afraid or embarrassed to disclose their illness at work, and to family or friends?
- Who was most likely to seek treatment in an emergency room? Who lacked access to medical care? Where was medical care sought? Who had barriers such as transportation, insurance and other barriers to health care? Who delayed treatment?
- What were suspected sources of COVID-19?
Surveyors are in the process of following up with respondents from initial surveys.
"Our surveillance continues to give us insight into how the pandemic and COVID-19 illness, even several years after the start of the pandemic, still affect people's lives," Fleischer said. "The COVID-19 illness and the pandemic have been experienced differently for Michiganders, including based on where they live in the state."
More information: Report: sph.umich.edu/mi-cress/pdf/MIC … s_Report_Aug2023.pdf