This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Study shows that new protocols enable many patients to safely return home just one day after lung cancer surgery
Thoracic surgeons and researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have found that increasing numbers of patients undergoing cancer-removal lung surgery by "anatomic lung resections"—lobectomies or segmentectomies—are able to go home safely and without complications one day after the operation, thanks to growing rates of robot-assisted surgeries and improvements in patient-centered care protocols.
However, the research team found, patients of lower socioeconomic status were considerably less likely than others to be discharged on postoperative Day 1 (POD1).
"We believe this is the first study to explore the impact of socioeconomic factors on POD1 discharge in this patient population," said Dao Nguyen, M.D., Sylvester Thoracic Cancers Group Co-Lead, and senior author of an article in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Open (JTCVS Open).
"We found that economic deprivation severely affects the ability to be discharged home the day following surgery, an observation that provides future direction for research and the development of improved care strategies and interventions," added Nguyen, who treats and studies lung and other cancers. The retrospective study of medical records of 750 patients over a 10-year period was launched to document the effects and progress of postoperative care protocols initiated by lung cancer surgeons at Sylvester.
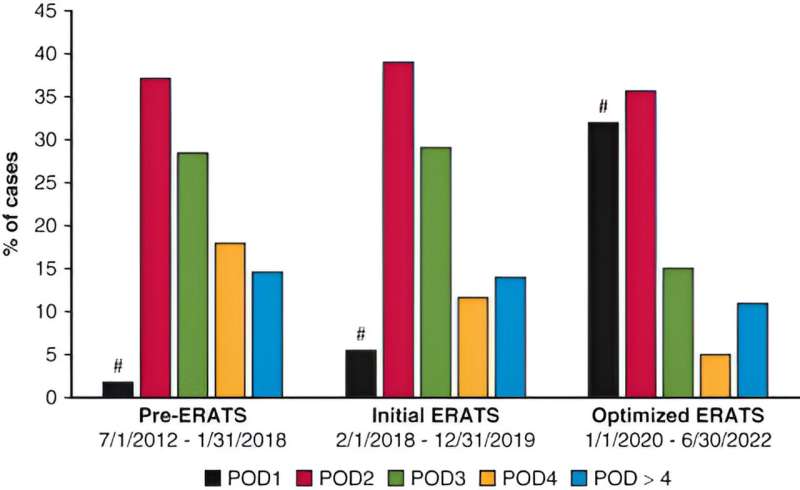
The guidelines, similar to those at other institutions, are called enhanced recovery after thoracic surgery, or ERATS, protocols. The first ERATS initiative was introduced in February 2018, with an optimized version implemented in January 2020. This study focused on findings from 279 patients whose treatment took place during the latest protocol period.
"Patients in the optimized ERATS group had significantly shorter hospital stays, more 'lung-sparing' procedures, and lower incidence of complications. Up to 30% of our patients undergoing robotic surgery and having the advantage of our latest ERATS version were discharged home on POD1. This is a significant difference from the less than 5% rate of POD1 discharge prior to the implementation of the optimized ERATS in January 2020," Nguyen said, adding that ERATS implementation has been associated with a significant reduction of postoperative acute pain and the need for in-hospital opioid medication.
Postoperative Day 1 discharge was a byproduct, not a stated goal, of ERATS, the authors note. The protocol's emphasis on an enhanced recovery period—in particular, effective opioid-sparing pain control and reduction of complications—brought about accelerated discharges, include those on POD1.
The study was based on the experience of thoracic surgeons, Nguyen and article co-author Nestor Villamizar, M.D. They had seen that POD1 discharge was possible and safe for patients undergoing other chest operations before extending the expedited discharge practice to the lung cancer surgery population.
According to the authors, critical factors making next-day discharge possible are: expedited drain removal, better opioid-sparing pain control, preoperative counseling to discuss realistic post-op expectations and home care arrangements, and regular, follow-up phone calls by nurse practitioners to encourage patients and monitor their progress.
Despite the growing number of next-day discharges, Nguyen and colleagues said they saw a 71% decrease in POD1 discharges in patients of lower socioeconomic status, a finding that demands further study. As part of their work, they also analyzed numerous factors contributing to and detracting from POD1 discharge.
"We were able to identify a variety of factors that can be mitigated to facilitate POD1 discharge, and we have instituted strategies to address them," Nguyen said.
Nguyen is senior and corresponding author. Daniel Gross, M.D., is first author. In addition to Villamizar, co-authors include: Ahmed Alnajar, M.D., Luis Miguel Cotamo, and Michael Sarris-Michopoulos.
More information: Daniel J. Gross et al, Postoperative day 1 discharge following robotic thoracoscopic pulmonary anatomic resections in the era of enhanced recovery protocol: A single-institution experience, JTCVS Open (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.xjon.2023.08.006