This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
AI combines chest X-rays with patient data to improve diagnosis
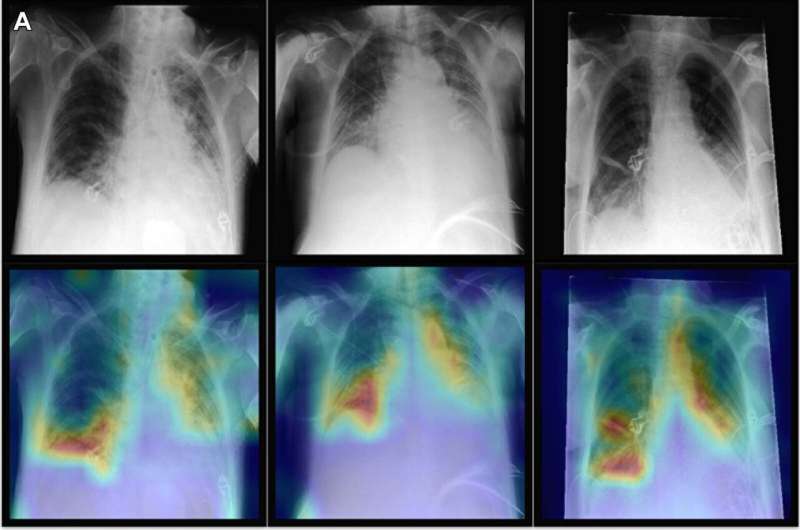
A new artificial intelligence (AI) model combines imaging information with clinical patient data to improve diagnostic performance on chest X-rays, according to a study published in Radiology.
Clinicians consider both imaging and non-imaging data when diagnosing diseases. However, current AI-based approaches are tailored to solve tasks with only one type of data at a time.
Transformer-based neural networks, a relatively new class of AI models, have the ability to combine imaging and non-imaging data for a more accurate diagnosis. These transformer models were initially developed for the computer processing of human language. They have since fueled large language models like ChatGPT and Google's AI chat service, Bard.
"Unlike convolutional neural networks, which are tuned to process imaging data, transformer models form a more general type of neural network," said study lead author Firas Khader, M.Sc., a Ph.D. student in the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at University Hospital Aachen in Aachen, Germany. "They rely on a so-called attention mechanism, which allows the neural network to learn about relationships in its input."
This capability is ideal for medicine, where multiple variables like patient data and imaging findings are often integrated into the diagnosis.
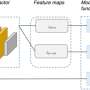
Khader and colleagues developed a transformer model tailored for medical use. They trained it on imaging and non-imaging patient data from two databases containing information from a combined total of more than 82,000 patients.
The researchers trained the model to diagnose up to 25 conditions using non-imaging data, imaging data, or a combination of both, referred to as multimodal data.
Compared to the other models, the multimodal model showed improved diagnostic performance for all conditions.
The model has potential as an aid to clinicians in a time of growing workloads.
"With patient data volumes increasing steadily over the years and time that the doctors can spend per patient being limited, it might become increasingly challenging for clinicians to interpret all available information effectively," Khader said. "Multimodal models hold the promise to assist clinicians in their diagnosis by facilitating the aggregation of the available data into an accurate diagnosis."
The proposed model could serve as a blueprint for seamlessly integrating large data volumes, Khader said.
More information: Firas Khader et al, Multimodal Deep Learning for Integrating Chest Radiographs and Clinical Parameters—A Case for Transformers, Radiology (2023).