This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New study gives hope to patients with medically unexplained physical symptoms
Medically unexplained physical symptoms (MUPS) are characterized by persistent bodily symptoms and functional impairment that lack an explanation through known medical condition or pathology.
It is estimated that up to 40% of all consultations in primary care in Norway involve patients presenting with MUPS and make up a considerable proportion of people on long-term sick leave and on disability.
Former studies have shown that the general practitioner (GP) often struggle to treat these patients without a defined diagnosis.
This often leads to frustration for both patients and physicians, with patients experiencing dissatisfaction with their medical treatment, feelings of stigmatization, and a sense of not being taken seriously.
GP Cathrine Abrahamsen has through her Ph.D. work at the Department of General Practice, University of Oslo, developed and tested the communication tool in question. The approach, grounded in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) principles but specifically tailored to the primary care context, helps patients to emphasize possibilities rather than limitations.
"As far as we are aware, this is the first primary care intervention with a structured communication tool with a work-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy approach, to show such significant results. Although CBT has demonstrated effectiveness in specialized settings, its efficiency in primary care has been relatively limited," Abrahamsen says.
Sick leave reduced by 27%
One-hundred three GPs from across the country were recruited for the study. Half of the GPs were trained in using the newly developed approach "ICIT"—Individual Challenge Inventory Tool.
The GPs recruited a total of 541 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 238 of these were treated with ICIT, while the remaining 303 made up the control group and received usual care.
"What makes this study unique is that it is specifically tailored to assist GPs in efficiently managing patients with MUPS. It is the GP who treats, and patients are selected based on those who have booked an appointment with the doctor. No patients were invited to see the GP for the purpose of the study," Abrahamsen explains.
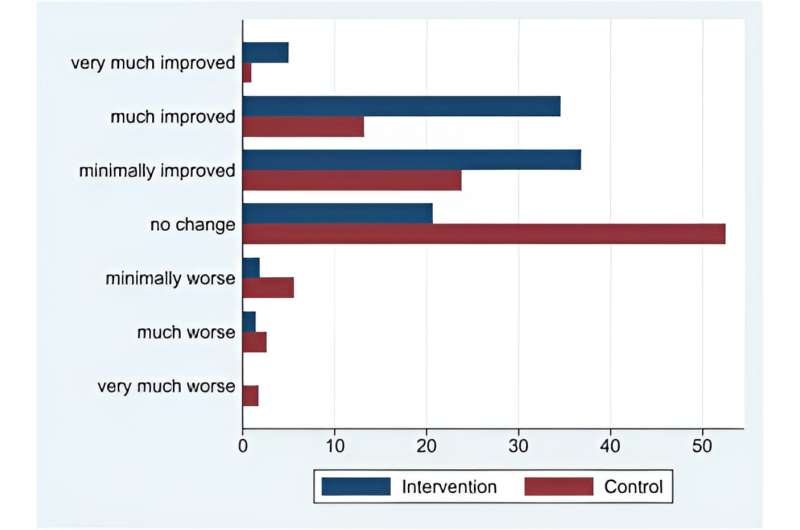
The results of the study are significant. Of the people in the intervention group, 76% reported an improvement in quality of life, compared to 38% in the usual care group. After 11 weeks the patients in the intervention group had a 27% reduction in sick leave, compared to 4% in the usual care group. These results are published in the journal eClinicalMedicine.
"The foremost aim of the study is to empower patients, helping them enhance their coping skills in both their daily lives and work settings. Patients with MUPS frequently experience psychological distress, social isolation, and a decline in their overall quality of life, resulting in high health care utilization and costs associated with sick leave," Abrahamsen says.
More information: Cathrine Abrahamsen et al, The effects of a structured communication tool in patients with medically unexplained physical symptoms: a cluster randomized trial, eClinicalMedicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102262