This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
'Zoom fatigue': Exhaustion caused by video conferencing proven on a neurophysiological level

Using EEG and ECG data, researchers at the University of Applied Sciences Upper Austria and Graz University of Technology were able to prove that video conferences and online education formats lead to greater fatigue than face-to-face alternatives.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the increase in virtual interactions has created a new challenge: fatigue caused by video calls, also known as Zoom fatigue or videoconference fatigue. This exhaustion, characterized by a feeling of tiredness and alienation due to too long or inappropriate video-based communication, had previously only been investigated through surveys and self-assessments by users.
An interdisciplinary research team led by René Riedl from the University of Applied Sciences Upper Austria/Campus Steyr and Gernot Müller-Putz from Graz University of Technology has now managed to provide neurophysiological evidence of videoconference fatigue.
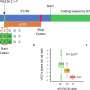
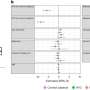
In the "Technostress in Organizations," project the researchers conducted a neuroscientific study with students to investigate videoconference fatigue in the context of online university lectures. The study participants took part in lectures that were held both in-person in a traditional lecture hall and online via video conferencing. These two experimental conditions were then compared with each other.
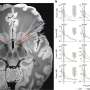
The research team measured fatigue parameters both neurophysiologically based on electroencephalography (EEG) and electrocardiography (ECG) and by questionnaires. This allowed them to record objective physiological parameters and subjective perceptions.
The objective findings based on EEG and specific parameters of heart rate variability as well as the subjective perceptions of the respondents showed that a 50-minute video conference-based lecture exhausted the study participants significantly more than a lecture of the same length in the traditional lecture hall format, where lecturers and students meet face to face. The study has been published in Scientific Reports.
"A better understanding of videoconference fatigue is important, as this phenomenon has a far-reaching impact on the well-being of individuals, interpersonal relationships and organizational communication," emphasizes René Riedl. Gernot Müller-Putz further explains that "a holistic view of the underlying psychological and physiological mechanisms is required to develop effective strategies for coping with the harmful effects of videoconference fatigue."
Together with two North American colleagues, the two scientists constitute the board of the Society for Neuro-Information Systems, a non-profit international scientific association based in Vienna that promotes and supports research and innovation at the intersection of neuroscience, information systems research and digitalization.
A key aim of this society is to make people more satisfied and productive when using digital technologies. "A better understanding of the neurophysiological processes in the body and brain of users is essential to achieve these goals," the two scientists conclude.
More information: René Riedl et al, Videoconference fatigue from a neurophysiological perspective: experimental evidence based on electroencephalography (EEG) and electrocardiography (ECG), Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45374-y