This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Correlation between the HALP Score and left ventricular hypertrophy in older patients with hypertension
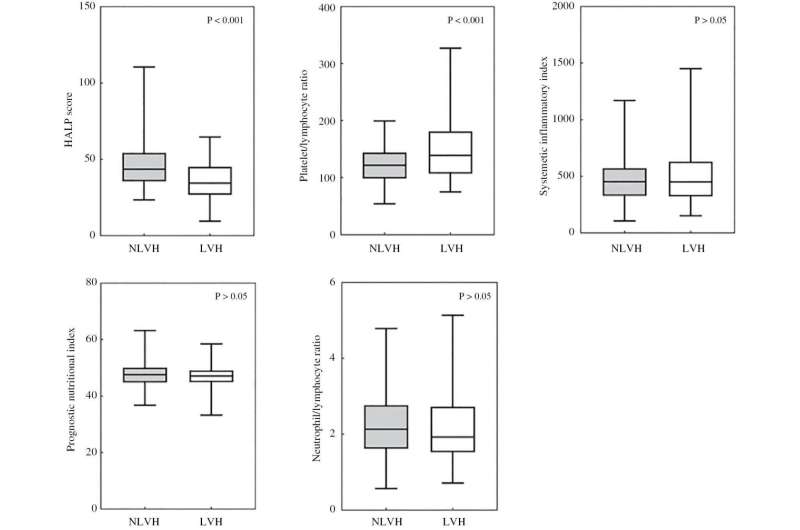
Hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) have emerged as significant risk factors for cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality. Inflammation and nutrition play critical roles in the development of hypertension and damage to target organs. The HALP Score, which assesses levels of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocytes, and platelets, is an index closely associated with inflammation and nutrition, and has been demonstrated to be particularly effective in the older population.
The objective of a new study by researchers in China was to examine the correlation between the HALP Score and LVH in older patients with hypertension. The study is published in the journal Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications.
Data from 234 patients with a mean age of 72 years, including clinical data, were collected and retrospectively analyzed and also routine blood, liver function, kidney function, and cardiac ultrasound parameters. All patients were categorized into a non-left ventricular hypertrophy (NLVH) group (n = 131) or an LVH group (n = 103). The association between the HALP Score and LVH was investigated, and potential influencing factors were considered.
The LVH group had a significantly lower HALP Score than the NLVH group. Logistic regression analysis revealed that a lower HALP Score and female sex were independent factors associated with LVH in older patients with hypertension (OR = 0.944, 9.962, 95% CI: 0.910–0.979, 3.866–24.300, P = 0.002, <0.001). The area under the curve for the HALP Score in diagnosing LVH in older patients with hypertension was 0.708 (95% CI: 0.641–0.776, P = 0.002).
The HALP Score is significantly associated with LVH in older patients with hypertension: lower scores indicate a greater likelihood of LVH. The HALP Score has moderate diagnostic value for LVH in this population.
More information: Yingfang Liu et al, Correlation between the Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, and Platelet (HALP) Score and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Older Patients with Hypertension, Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (2023). DOI: 10.15212/CVIA.2023.0068