This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
AI trained on X-rays can diagnose medical issues as accurately as doctors, finds study
A collaborative study among Warwick, King's College London and several NHS sites has demonstrated how AI can analyze X-rays and diagnose medical issues just as accurately or more accurately than doctors.
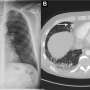
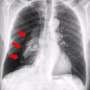
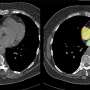
The AI software can scan X-rays as soon as they are taken for possible conditions and flags any abnormalities. It then gives a percentage chance of each of the abnormalities being present. The AI also understands the seriousness of the different conditions and flags the more urgent ones to doctors accordingly.
"Current AI programs available to us in the NHS only have a limited scope. Comprehensive AI programs like this will be the future of medicine, with AI acting as a co-pilot for busy doctors. With the acute shortage of radiologists in the UK, programs like this will facilitate interpretation and reduce delays for diagnosis and treatment," commented co-author Professor Vicky Goh of King's College London, and immediate past Chair of the Academic Committee at the Royal Society of Radiologists.
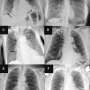
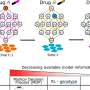
The AI was trained on 2.8 million historic chest X-rays from over 1.5 million patients and can scan X-rays for 37 possible conditions.
It was just as accurate or more accurate than the doctor's analysis at the time the X-ray was taken for 35 out of 37 conditions (94%).
The program also uses a large language model to understand the historical reports written by clinicians—the same underlying technology used by other AI programs, such as ChatGPT.
To verify the accuracy of the AI, a sample of over 1,400 X-rays it had analyzed was cross-examined by a group of senior radiologists, who compared the diagnoses made by the AI with the historical diagnoses by radiologists at the time.
Dr. Giovanni Montana, Professor of Data Science at Warwick, and lead author, suggested that the AI tool could either be used as a screening tool for radiologists or to offer "the ultimate second opinion," avoiding human bias.
Dr. Montana commented, "This program has been trained on millions of X-rays and is highly accurate. It eliminates the element of human error, which is unavoidable, and bias. If a patient is referred for an X-ray with a heart problem, doctors will inevitably focus on the heart over the lungs. This is totally understandable but runs the risk of undetected problems in other areas. This AI eliminates that human bias—it's the ultimate second opinion."
There is also the possibility that the AI could look at the X-rays where no abnormalities are found, which is around half of them, and flag this to doctors in a way that could improve efficiency for the NHS. By allowing AI to weed out X-rays with no abnormalities found, radiologists will have more time to focus on challenging and more critical tests.
This AI software—entitled X-Raydar—is designed to help reduce the workload for doctors and cut delays. Remarkably, the research group has open-sourced the entire software for non-commercial uses to speed up the pace of research development in this domain.