This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Cancer grade probing system method evaluates model tumor malignancy
An important part of choosing the most suitable cancer therapy is understanding the malignancy of the tumor; however, current methods for evaluating brain tumor malignancy are invasive and have a high risk of complications.
Researchers, led by Professor Yasuchika Hasegawa and Professor Shinya Tanaka of the Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) at Hokkaido University, have developed a non-destructive cancer grade probing system (GPS) for evaluating the malignancy grade of model glioma tumor cells using a water-soluble, luminescent europium complex. This method could lead to non-invasive tests for the determination of tumor malignancy in patients. The work has been published in Scientific Reports.
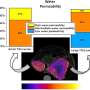
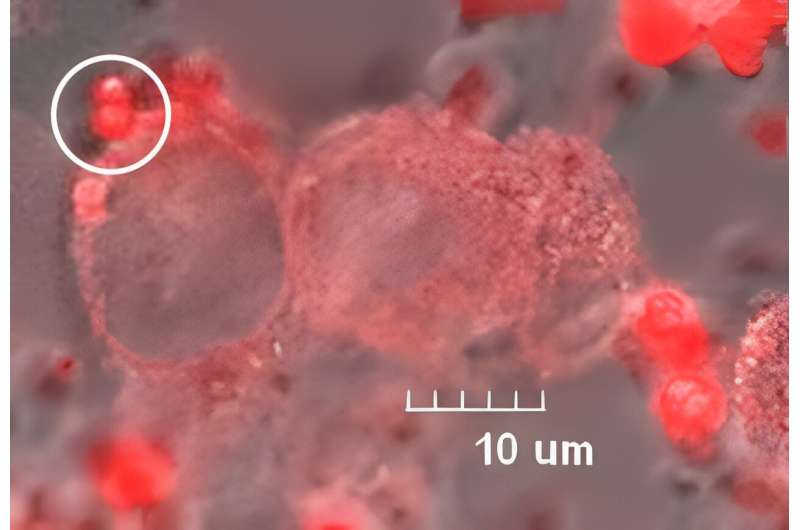
The team evaluated tumor malignancy by introducing the europium complex to model cells that mimic glioma, a common type of tumor that accounts for 26.3% of brain cancers. Three different model cells that mimic different grades of malignancy were tested, and researchers measured changes in the lifetime of the europium complex's characteristic red-light emission.
Researchers found that during the first three hours after adding the europium complex, larger changes in the lifetime of the light emission occurred in the more malignant cells.
"Visualization of cancer cells using luminescent complexes has previously been reported, but our hypothesis was that the photophysical signals sent by such complexes in cancer cells might reflect internal information from the cancer cells," said Hasegawa.
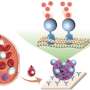
To achieve this result, researchers first modified the europium complex so that it would be water soluble and stable among the amino acids in the cell culture medium. Upon addition to the cell culture medium, the europium complex initially forms an aggregate with itself.
Interaction with model tumor cells results in the aggregates breaking into single molecules, which are then rapidly taken up by the cells. This process promotes structural changes in the europium complex, which cause changes in the lifetime of the complex's red-light emission.
These differences in emission lifetimes were attributed to the varying tumor activity and growth processes of the different malignancy grades, which could cause different structural changes at different time scales in the europium complex. The team anticipates that using this method could enable continuous detection of tumor activity and provide doctors with key information when deciding appropriate treatment.
"Brain tumors occur in 4.6 out of every 100,000 people in Japan, and the five-year survival rate is 16% for the most malignant grade 4 type of glioblastoma, which is an aggressive type of glioma brain tumor," explained Tanaka. "The malignancy evaluation method we developed may be able to benefit these patients in the future."
More information: Mengfei Wang, et al. Structure-changeable luminescent Eu(III) complex as a human cancer grade probing system for brain tumor diagnosis, Scientific Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50138-9